Bladder reconstruction - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title: Bladder reconstruction
1
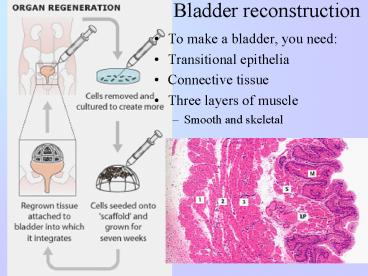
Bladder reconstruction
- To make a bladder, you need
- Transitional epithelia
- Connective tissue
- Three layers of muscle
- Smooth and skeletal
2
Urothelium/transitional epithelium
- Scalloped when relaxed
- Flattened when distended
- Many intermediate filaments
- Can see plaques
- Intramembranous proteins that cytoskeletal
proteins attach to
relaxed
distended
Plaques indicated by arrows
3
Neuronal Patterning
4
A Neuron Primer
5
Nerve cell morphology
6
Morphology examples
7
Perikaryon or soma
- Large nucleus
- Prominent nucleolus
- Nissl (ribosomes and rER)
8
Neuronal Processes
- Axons
- impulses travel away from the cell body
- Only one per cell
- diameter constant along length
- Dendrites
- impulses travel toward cell body
- Taper gradually
Neuropil
9
Gray matter of the CNS
- Nerve cell bodies
- Protoplasmic astroglia
- (oligodendroglia?)
- Neuropil
- Between neuron cell bodies
- Axons, dendrites and glial cells
10
Classification of Cell Renewal
- Nonrenewing or Permanent or Static Cells
- Permanent G0 phase
- Potentially renewing or Expanding or Stable Cells
- Long G0 phase
- Continuously renewing or Labile Cells
- Short G0 phase
- Division and Interconversion
11
(No Transcript)
12
Nonrenewing or Permanent cells
- No proliferative capacity whatsoever
- Never seem to divide
- Irreplaceable
- Have a long life span and live in protected
environments - Scientists now finding exceptions
13
Examples
- Nerve cells
- nerve fibers have regenerative potential
- Cardiac muscle cells
- Auditory hair cells of the ear
- Lens cells of the eye
14
Our Neurons
- Primary culture from neonatal rat brain (Brain
Bits) - From the cortex
- Contains maybe about 10 astrocytes
- Using serum would select for astrocytes
- Use Neurobasal medium and B27 instead
15
Practical issues in handling E18 cortical cells
- Kept cold but not frozen
- Cells do not multiply
- Passaging them does not make sense
- Can be cultured for up to one (1) month
- Use Neurobasal media
- B27-a serum free supplement
- Glutamine
- Change only ½ media at a time
- Must seed at a low density to see the pattern
- Usually require a feeder layer of glial cells
- But we wont use one
16
Interesting side notes
- If you want to study neuron response to free
radicals, buy B-27 without antioxidants - minus vitamin E, vitamin E acetate, superoxide
dismutase, catalase and glutathione - If you want to prevent neural differentiation of
stem cells, buy B-27 without vitamin A - Retinoic acid is a common differentiation inducer
- Q can you name another common inducer of
differentiation? - Dexamethasone (DMSO, hydrocortisone too)
- In what lab was that inducer important?
- Adipocyte differentiation
17
Cell Response to Feature Size
- Container walls can dictate where cells grow
- 5mm channels encourage cells to grow inside the
channel - gt5mm cells spread like they are in a culture dish
- lt5mm cells grow over the feature
- Optimal sized patterns for neuron growth
- 5mm wide
- 120mm x 80mm long
18
Protein Microstamping
PDMS Microstamp
Stamp substrate
Soak in Polylysine
Soak in SDS
http//soma.npa.uiuc.edu/labs/wheeler/current20pr
oject/sld001.htm
19
The Role of SDS
- Pretreatment with SDS
- Ease of protein release from stamp
- Creates well defined patterns
- Extends stamp life
Chang et al. Biomaterials 2003 24(17) 2863-70
20
The Role of Poly-D-Lysine
- Using as an ink for our microstamps
- Free amine groups offer a hydrophilic surface for
preferential cell attachment - Neurons will migrate to areas of higher
poly-D-lysine concentration
O H H
( C C N )n
CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 NH3
21
Microelectrode Array
60 metal electrodes integrated micrometer size
(single neuron) Multi-site monitoring
Extracellular recording and stimulation Bio-Electr
onic Hybrid system Integration with electronic
device We are NOT using this!!
http//soma.npa.uiuc.edu/labs/wheeler/current20pr
oject/sld001.htm
22
Neuronal Network Activity
http//soma.npa.uiuc.edu/labs/wheeler/current20pr
oject/sld001.htm
23
Possible Applications
- Allows for investigation into neural development
- Allows for probing of neural learning and memory
- Development of neural tissue for tissue
engineering - Cell-based biosensors
- Biocomputing
- Acknowledgements
- Betty Ujhelyi
- Dr. Bruce Wheeler and his laboratory
24
Other Tasks This Week
- Feed 2 and 3 week osteoblasts
- Seed 1wk diff and 1wk undiff D1 OR UVAs
- Observe ORS colonies on feeder plate--photograph
25
Other practical considerations
- Acetone dissolves plastic!
- Use glass pipets
- Dont rinse stamp in the 6cm dish
- Save the glass pipets
- Return to the side bench
- Dont throw in trash can or sharps box
26
What your colonies should look like
10x
20x