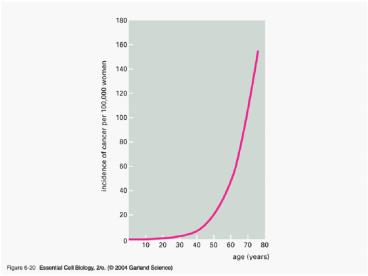
06_20_cancer_age.jpg
1 / 25
Title: 06_20_cancer_age.jpg
1
06_20_cancer_age.jpg
2
- Gene Mutation Origins and Repair Processes
GAATTC ? GTATTC A ? a
Skin cancers from Xeroderma pigmentosum, a
recessive hereditary disease caused by a
deficiency in a DNA repair enzyme
3
Mutations
Transcription Translation
Gene
DNA
Normal protein gene product
Mutational event
Mutated gene
- Abnormal protein
- gene product
- partially functional
- nonfunctional
- no gene product
- Gene
- nucleotide sequence on a
- chromosome that encodes
- a specific protein
4
DNA Mutations An Overview
5
Mutations
Heritable changes in base sequences that modify
the information content of DNA
Forward mutation a mutation that changes the
wildtype allele of a gene to a different allele.
The resultant allele can be either dominant or
recessive to the original wildtype
Reverse mutation or reversion a mutation that
causes a mutant allele to revert back to
wildtype.
Remember wild alleles designated with a
6
La mayoría de las mutaciones ocurre durante la
replicación del DNA o durante su reparación
7
Mistakes during DNA replication can also alter
genetic information
Replication errors are extremely rare, generally
occurring once per 109 base pairs
The rate of replication errors is kept low due to
correction or proofreading activity, which
reduces the error rate to one in 106 bases copied
by DNA polymerase (in vitro)
Both DNA polymerase I and II have
proofreading ability. It is a 3 to 5 nuclease
activity
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
Classes of DNA mutations
Substitution base at certain position is
substituted by one of other 3 bases
Transition purine (A/G) for purine or pyrimidine
(C/T) for pyrimidine
Transversion purine (A/G) to pyrimidine (C/T) or
visa versa
11
Deletion Mutation block of ONE or
more nucleotide pairs is lost from a DNA molecule
12
- Inversion Mutations
- 180 rotation of segment of DNA molecule
- Translocations
- Parts of nonhomologous chromosomes change place
13
Overview
- Hereditable change in DNA resulting from change
in nucleotide sequence - Mutation changes one allelic form to another and
is the ultimate source of genetic variation. - Mutational variation underlies the study of
genetics. - Mutations are produced by mutagens or occur
spontaneously. - Each base pair has a certain probability of
undergoing change - Point mutations include single base-pair
substitutions, additions or deletions. - Specialized forms of mutation include expansion
of trinucleotide repeats and insertion of
transposable elements. - Many types of mutation can be repaired.
14
Mutation
- Hereditable change in DNA resulting from change
in nucleotide sequence - Multiple causes
- DNA replication/repair errors
- Mutagens spontaneous DNA damage
- Insertion of transposons
- Several categories of mutation
- Point mutations
- Swap one base for another insert a base delete
a base - Alter the number of copies of a short repeat
- Large insertions into a gene
15
Point Mutations
- Single or few base pair changes
- Provide background rate of mutation
- critically important to evolution
- More likely to lead to loss of function than gain
of function - Origin of point mutation
- Induced, by geneticist for example
- action of mutagen environmental agent that
alters nucleotide sequence - process of inducing mutations by mutagens called
mutagenesis - Spontaneous
- arise in absence of known mutagen
- may be caused by errors in DNA replication
16
Types of point mutation
- Base substitution
- transition
- A ? G (purine ? purine) (AT ? GC)
- C ? T (pyrimidine ? pyrimidine) (CG ? TA)
- transversion
- purine ? pyrimidine (e.g., A ? C) (AT ? CG)
- Addition or deletion of nucleotide pairs
(base-pair addition or deletion) - also called indel mutations
17
Molecular Consequences
18
Terminación Prematura por mutaciones sin
sentido (non sense)
19
(No Transcript)
20
Mutaciónes supresoras intragénicas
21
Figure 27.27 How an intergenic suppression
mutation can overcome a nonsense mutation.
22
(No Transcript)
23
Efecto de mutaciones supresoras intergénicas
24
Mutación supresora Ambar
25
Mutación supresora Opalo