The - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title: The
1
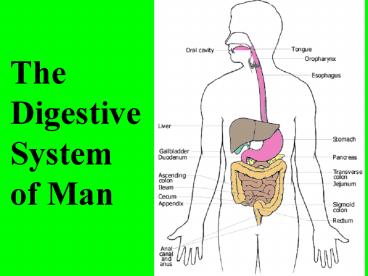
The Digestive System of Man
2
The Digestive System
- It is also known as the Alimentary Canal.
- Food undergoes four major processes
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Metabolism
- Assimilation
3
The Lower Part of the Digestive System
4
Mouth
- There two major processes which take place
- Mastication (Chewing)
- - Breaks down large food molecules.
- - Increases surface area of food particles.
- Secretion of Saliva
- - Contains salivary amylase (ptyalin) that
- digests starch to maltose.
- - Provides an alkaline medium.
- - Lubricants and moistens food.
5
Esophagus
- It is a mucus muscular membrane lined tube.
- There occurs a process known as Peristalsis.
Peristalsis It is an involuntary process of
muscular contraction forcing the bolus (food)
down to the stomach.
6
Stomach
- It secretes two substances
- Gastric juice
- It contains 2 enzymes namely
- - Pepsin for digestion of proteins to
peptides. - - Rennin for solidifying milk protein in
young. - Hydrochloric acid
- - Kills bacteria in food.
- - Provides an acidic media
- - Stimulates stomach walls
- to secrete more gastric juice.
7
Duodenum
- It receives
- Bile
- Its a non-enzymatic green fluid
- - Breaks down fats into tiny droplets.
- - Provide alkaline media.
- Pancreatic juice
- - Pancreatic amylase for digestion of starch.
- - Lipase for digestion of fats.
- - Trypsin for digestion of proteins.
8
Ileum
- Its walls secretes intestinal juices which
contain - enzymes to complete digestion
- Sucrase for digestion of sucrose to
- glucose and fructose.
- Lactase for digestion of lactose to
- glucose and galactose.
- Maltase for digestion of maltose to
- glucose molecules.
- Erepsin for digestion of peptides
- polypeptides to amino acids.
- Lipase for digestion of lipids to
- fatty acids glycerol.
9
Liver
- It is the largest organ in the mammalian body.
- It secretes bile which is stored in the gall
bladder. - Bile breaks down fats into tiny droplets
through - emulsification.
- Roles
- Regulates sugar/glucose.
- Breaks down excess RBC.
- Storage of blood.
- Detoxification.
- Generation of heat
10
Pancreas
- It is an endocrine gland
- because it secretes Insulin
- hormone - converts excess
- glucose into glycogen for
- storage.
- It is also an exocrine gland because it secretes
- pancreatic juice in the duodenum
- - pancreatic juice contains lipase, trypsin
and - pancreatic amylase for digestion of lipids,
- proteins and starch.
11
Absorption
- It occurs within
- the ileum in
- finger-like
- projection
- known as
- Villi.
12
Villi
- Amino acids and simple sugars like glucose,
- fructose diffuse through thin Epithelial cells
into - the blood capillaries.
- Fatty acids and glycerol enter the Lacteal into
- the lymphatic system then finally into the
blood - system through the Innominate vein.
13
Adaptations of Ileum
- It is very long and wound to increase surface
area. - It has millions of villi for food absorption.
- Numerous blood capillaries for carrying of
- amino acids and simple sugars.
- Lacteal for fatty acids and glycerol
absorption. - Thin epithelial cells through which soluble
foods - easily diffuse.
- Goblet cells secrete mucus which prevents
enzymes - from digesting ileum walls.