GLAST MASTER
1 / 11
Title: GLAST MASTER
1
(No Transcript)
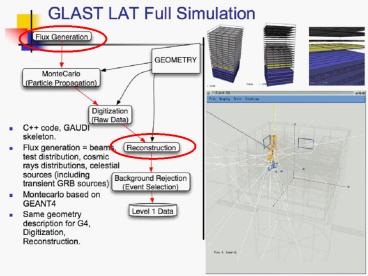
2
Structure for celestial source simulators
- The development of a celestial source model for
GLAST/LAT software implies - Capability to use the models within the full
Monte Carlo of the LAT instrument (GLEAM) - Capability to use the models within
observationSim, the science simulator. - Satisfy requirements in the structure of the
software (interface with the Flux package,
which has the responsibilities to feed the
simulation with the photon extracted from the
source). - INFN-Pisa responsibility
- Gamma-Ray Bursts simulators
- the GRB physical model
- GRB phenomenological model
- High level Pulsars simulations (polar cap -
outer gap model) - These sources are used by the GLAST community and
are included in the Data Challenges.
3
GRB - Simulation of the engine
Phenomenological approach
Parameters from observed distributions
(BATSE) Different GRB light curves can be
obtained. Fluxes are normalized to the BATSE
observed fluence distribution (BATSE
catalogue) LAT photons are extracted from the
predicted (extrapolated) flux and processed by
the GLAST/LAT Montecarlo.
Physical approach
Fireball model (Piran,1999) Shells emitted with
relativistic Lorentz factors Internal shocks
(variability naturally explained) Acceleration of
electrons between with a power law initial
distribution, between ?min an ?max Non-thermal
emission (Synchrotron and Inverse Compton) from
relativistic electrons
4
Gamma Ray Bursts Spectral Studies
High energy cutoff
- GLAST/LAT will be able to study the high energy
spectrum of GRB, recognizeing the cut-off up to
energy above 10 GeV for single bursts. - Information on the Lorentz Factor of the
expanding shells
Self Synchrotron Compton
- GLAST/LAT detector will have the requirements
for detecting the high energy component and to
localize the SSC peak of the vFv spectrum - The Inverse Compton component does not affect the
BATSE energy range !
Band Function best representation of the GRB
flux between 20 keV and 1 MeV
High energy photons (gt50 MeV)
5
Timing studies - Quantum Gravity effect
6
Some results - GLAST Sensitivity for GRB
- Alerts algorithm sensitivity 5 photonsgt100 MeV
- Effective area for on-axis and off-axis
observations - Simulated BATSE catalog (with the observed
fluence distribution) and extrapolation to LAT
energies using the GRB physical model.
- LAT will detect 90 of the BATSE-like bursts if
they are on-axis, and 50 if they are off-axis
(67)
- LAT sensitivity as a function of the Inverse
Compton emission
Low IC High IC
7
On going Italian activities (GRB)
- GRB simulations
- Development of the models (adding models,
refinement of the already existing models) - Preparation for the Data Challenge 2
- Development of analysis tools
- Visualization, spectral fitting and temporal
analysis - GRB dedicated analysis (high energy cut-off,
Diffusion Entropy,) - GRB trigger and alert algorithms
- On-board reconstruction
- Determination of the modified IRF for an
optimized selection cuts - GLAST/LAT GRB Science
- Coordination of the GLAST/LAT science group
(Nicola Omodei) - Publication plan before the launch
- GRB modeling and simulations
- GRB analysis tools development
- GLAST sensitivity to GRBs
- Cosmological use of Gamma-Ray Bursts, Quantum
gravity, etc.
8
g ray pulsar simulation for GLAST
- PulsarSpectrum is a simulator developed in Pisa
that is being used to simulate gamma ray emission
from pulsars - Key features
- It can reproduce spectra and lightcurves of known
g ray pulsars - Flexible architecture to facilitate creation of
pulsar sources - Advanced simulation of timing effect due to
period changes and motion of GLAST and Earth in
Solar System - Full phenomenological model now implemented
- Pulsar parameters easy to implement
- Capability of simulation of pulsar catalogs in
order to perform population studies - Fully compatible with GLAST-LAT standard software
environment (Gleam, observationsSim)
9
The phenomenological model
This model takes a lightcurve and a spectrum
compatible with observations and combines them to
obtain a 2-dimensional matrix
(ph/keV/s/m2)
10
PulsarSpectrum and LAT
- Some examples
11
Pisa activities on pulsars
- Status of work
- Full simulation code implemented and tested
- Phenomenological model included
- Simulation of period change with time
- Effects of GLAST and Earth motion and of
gravitational field of Sun on timing (barycentric
de-corrections) - Simulation of EGRET pulsars
- Use of PulsarSpectrum for testing the LAT
Analysis Tools for pulsars - Participation to Analysis Tools test campaigns
(Science Tools Checkouts). Up to now 1st and 2nd
Checkout - Development of visualization and analysis tool
(not included is the Analysis Tool suite) - Work on simulating catalogs of pulsars in
preparation for DC2
- Work in progress and plans for future
- Inclusion of more realistic timing effects
(timing noise, glitches,etc.) - Development of simulation of binary pulsar
systems - Work with LAT Pulsar Science Group for studying
GLAST performances on pulsar science - Study of analysis techniques for pulsar blind
searches - Work on the development to fit optimally the
requirements for DC2 (start January 2006) - Provide the ephemerides database of the simulated
pulsars to the DC2 users