8.1. Non-contrast CT Brain - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
8.1. Non-contrast CT Brain
Description:
8.2 Non-contrast CT Brain. Acute Subdural Hematoma: ... can produce herniation of the brain resulting in sudden decompensation of the ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1091
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 8.1. Non-contrast CT Brain
1
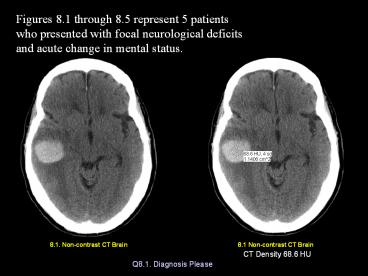
Figures 8.1 through 8.5 represent 5 patients who
presented with focal neurological deficits and
acute change in mental status.
8.1. Non-contrast CT Brain
8.1 Non-contrast CT Brain
CT Density 68.6 HU
Q8.1. Diagnosis Please
2
8.2. Non-contrast CT Brain
8.2 Non-contrast CT Brain
CT Density 72.9 HU
Q8.2. Diagnosis Please
3
8.3a. Non-contrast CT Brain
8.3bc. Non-contrast CT Brain
CT Density 25.0 HU
09/02/2003
09/21/2003
Q8.3. Diagnosis Please
4
8.4a. Non-contrast CT Brain
8.4b. Non-contrast CT Brain
8.4c. Non-contrast CT Brain
Q8.4. Diagnosis Please
5
8.5 Non-contrast CT Brain
Q8.5. Diagnosis Please
6
(No Transcript)
7
Figure 1 Acute intracerebral hematoma within
the right temporal lobe (arrow) with surrounding
edema (E). 60 year-old patient with melanoma.
Hemorrhage is from metastatic tumor bleed.
E
8.1 Non-contrast CT Brain
CT Density 68.6 HU (Hounsfield Units)
Acute Intracerebral hematoma Acute hematoma is
seen by non-contrast imaging as an area of high
density with density numbers ranging from 40 to
90HU. CT can detect acute intracerebral blood as
small as 2mm, due to contrast between
high-density of blood and low-density of
surrounding brain (arrows).
8
Acute Subdural Hematoma Subdural hematoma is
located between the layers of dura and arachnoid
mater, covering the cerebral hemispheres whereas
intracerebral hematoma is localized within the
brain substance. Acute subdural hematoma is
recognized by CT as an area of peripheral zone of
crescentic shaped increased density, outside the
surface of the brain (arrows). Most subdural
hematoma is caused by tear of bridging cortical
veins. Acute subdural hematoma can evolve over a
period of time and thus classified as acute,
subacute and chronic hematoma. Acute Subdural
Hematoma Up to 7 day old High CT density
(40-90HU) Subacute Subdural Hematoma (7 to 21
days old) The CT density of acute blood gradually
decreases and becomes isodense with adjacent
brain, thus less readily visible and can be
easily overlooked.
8.2 Non-contrast CT Brain
Acute subdural hematoma covering the right
cerebral hemisphere (arrows), more prominent
posteriorly. CT density of blood is 74HU
consistent with acute blood. Patient with
history of recent fall.
9
A Left frontal chronic subdural hematoma
(arrowheads) seen as an area of low-density with
crescentic inter margin, compressing the adjacent
brain. B Left frontal subdural hematoma was
completely evaluated using burr holes in the
skull, but the right chronic subdural hematoma
has increased in size in the follow-up CT done 19
days later (arrows) which was also subsequently
evaluated. 55 year-old patient with chronic
myelogenous leukemia with low platelet count.
8.3a. Non-contrast CT Brain
8.3bc. Non-contrast CT Brain
09/02/2003
CT Density 25.0 HU (Hounsfield Units)
09/21/2003
Chronic Subdural Hematoma Over 21 days old
Acute blood as it evolves, it undergoes
liquefaction, and also mixes with cerebrospinal
fluid from adjacent subarachnoid space, thus
converting into a serosanguineous fluid. This
fluid has low CT density reaching close or
similar to cerebrospinal fluid. Slow movement of
subarachnoid fluid into the subdural hematoma can
give rise to gradual expansion of subdural
hematoma that can exert mass effect upon the
adjacent brain with or without brain edema. This
can produce herniation of the brain resulting in
sudden decompensation of the patient leading to
coma. Thus even a chronic subdural hematoma
might need an emergent neurosurgical intervention.
10
8.4a,b,c. Non-contrast CT Brain
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Subarachnoid blood is
recognized by visualizing the high-density of
acute blood outlining the cerebral sulci and
subarachnoid cisterns.
Subarachnoid Blood Subarachnoid blood filling
the right cerebral sulci (arrow), related to
recent pituitary surgery
11
Shunt-induced (arrow), intraventricular blood
(v). Intraventricular blood is recognized by
replacement of normal CSF density by
high- density of blood.
v
Intraventricular Hemorrhage Intraventricular
blood is easily recognized by high-density blood
outlining the lateral ventricles, III ventricle
and IV ventricle.
8.5 Non-contrast CT Brain
12
Questionaire
8.6
Common cause of intracranial hemorrhage in a
county hospital emergency room. a) Rupture of
arterio-venous malformation b) Rupture of
cerebral aneurysm c) Trauma d) Hypertension e)
Stroke
13
Questionaire
8.6
Common cause of intracranial hemorrhage in a
county hospital emergency room. a) Rupture of
arterio-venous malformation b) Rupture of
cerebral aneurysm c) Trauma d) Hypertension e)
Stroke
14
Questionaire
8.7
Likely cause of nontraumatic intracranial
hemorrhage in an 8 year-old girl. a) Rupture
of arterio-venous malformation b) Rupture of
cerebral aneurysm c) Hypertension d) Stroke
15
Questionaire
8.7
Likely cause of nontraumatic intracranial
hemorrhage in an 8 year-old girl. a) Rupture
of arterio-venous malformation b) Rupture of
cerebral aneurysm c) Hypertension d) Stroke
16
Questionaire
8.8
35 year-old man developed severe headache and
drowsiness while having sex. The patient was
taken to the emergency room and a CT scan showed
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Most likely cause for
subarachnoid hemorrhage to be considered
is a) Rupture of arterio-venous
malformation b) Rupture of small vessel within
the brain from excitement, nothing to worry
about. c) Rupture of cerebral aneurysm d) Acute
migraine e) Stroke
17
Questionaire
8.8
35 year-old man developed severe headache and
drowsiness while having sex. The patient was
taken to the emergency room and a CT scan showed
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Most likely cause for
subarachnoid hemorrhage to be considered
is a) Rupture of arterio-venous
malformation b) Rupture of small vessel within
the brain from excitement, nothing to worry
about. c) Rupture of cerebral aneurysm d) Acute
migraine e) Stroke
18
Common Etiology for Nontraumatic intracranial
Hemorrhage
Congenital
Arterio-venous malformations Cerebral berry
aneurysms
Tumors
Primary Glioblastoma
Metastasis Melanoma Thyroid Carcinoma
Renal Cell Carcinoma Chorio Carcinoma
Vascular
Embolic Infarction Venous Sinus Thrombosis
Hypertension
Coagulopathy