1a. Internal Auditory Meatus - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
1a. Internal Auditory Meatus
Description:
4. Pterygopalatine Fossa Seen Through the Pterygomaxillary Fissure ... the infratemporal fossa by way of the petrotympanic fissure. ... 6. Petrotympanic fissure ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:705
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 1a. Internal Auditory Meatus
1
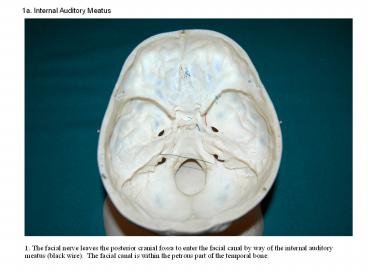
1a. Internal Auditory Meatus
1. The facial nerve leaves the posterior cranial
fossa to enter the facial canal by way of the
internal auditory meatus (black wire). The
facial canal is within the petrous part of the
temporal bone.
2
1b. Internal Auditory Meatus
The facial nerve leaves the posterior cranial
fossa to enter the facial canal by way of the
internal auditory meatus (black wire).
3
2. Hiatus of the Canal and Groove for the Greater
Superficial Petrosal Nerve
The greater superficial petrosal nerve leaves the
facial canal to enter the middle cranial fossa by
way of the hiatus of the canal for the greater
superficial petrosal nerve (black wire).
4
3. Pterygoid Canal at Anterior Lip of the
Lacerate Foramen
The greater superficial petrosal nerve is joined
by the deep petrosal nerve to form the nerve of
the pterygoid canal (black and red wire). This
nerve leaves the middle cranial fossa to enter
the pterygopalatine fossa by way of the pterygoid
canal. The posterior opening of the pterygoid
canal is at the anterior lip of the lacerate
foramen. The greater superficial nerve and the
deep petrosal nerve travel within the cavernous
sinus.
5
4. Pterygopalatine Fossa Seen Through the
Pterygomaxillary Fissure
The anterior opening of the pterygoid canal is
into the pterygopalatine fossa (black wire). The
pterygopalatine fossa is located medial to the
pterygomaxillary fissure and contains the
pterygopalatine ganglion.
6
5. External Auditory Meatus
The chorda tympani nerve leaves the facial canal
and crosses the middle ear (black wire). It
then leaves the middle ear to arrive in the
infratemporal fossa by way of the petrotympanic
fissure. This view shows the path of the chorda
tympani within the middle ear (seen through
external auditory meatus) and then entering the
infratemporal fossa through the petrotympanic
fissure.
7
6. Petrotympanic fissure
The chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve
enters the infratemporal fossa by way of the
petrotympanic fissure (black wire). Notice the
close relationship to the mandibular fossa. The
chorda tympanic is vulnerable to injury at this
loccation.
8
7. Stylomastoid Foramen
The facial nerve leaves the facial canal to enter
the parotid region by way of the stylomastoid
foramen (black wire).