Graphs and Data Tables - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
Graphs and Data Tables
Description:
... that are generally shiny, hard, ductile, malleable, and good conductors of electricity. ... Ductile = capable of being drawn into wires ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:65
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Graphs and Data Tables
1
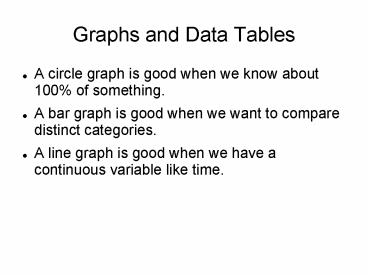
Graphs and Data Tables
- A circle graph is good when we know about 100 of
something. - A bar graph is good when we want to compare
distinct categories. - A line graph is good when we have a continuous
variable like time.
2
Atoms
- Atoms
- All things are made of atoms. Everything in the
world, including you, is made out of atoms. - Atoms are so small that they cannot be seen with
normal microscopes. - Ex) If a person could break a piece of iron into
its smallest parts, the person would be left with
____. - A) Protons C) Atoms
- B) Neutrons D) Quarks
3
Subatomic Particles
- Atoms are made of subatomic particles.
- There are three parts of subatomic particles
protons, neutrons, and electrons. - Ex) Which of the following is not a subatomic
particle? - A) Protons C) Electrons
- B) Neutrons D) Nucleus
4
Atomic Structure
- Protons and neutrons are located in the center of
an atom. This area is called the nucleus.
- Ex) Which of the following subatomic particles is
not located in the nucleus? - A) Proton
- B) Neutron
- C) Electron
5
Protons
- Protons
- Protons have a positive charge.
- Protons are located in the nucleus or center of
the atom.
6
Neutrons
- Neutrons
- Neutrons have a neutral or zero charge.
- Neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom
with the protons.
7
Electrons
- Electrons
- Electrons have a negative charge.
- Electrons are located outside of the nucleus.
- Electrons spin around the nucleus. You can think
of the nucleus as the sun and the electrons as
the planets. Just as the planets spin around the
sun, the electrons spin around the nucleus.
8
Atomic Number
- Atomic number is the number of protons in an
atom. If an atom has an atomic number of 5 then
the atom has 5 protons. - Ex) Atom 1 has 5 protons, atom 2 has 3 protons.
Solve this math problem Atomic Number of Atom 1
Atomic Number of Atom 2
9
History of Periodic Table
- History
- Dmitri Mendeleev came up with the first periodic
table of the elements in 1869. Mendeleev was a
Russian scientist. - Mendeleev arranged his atomic table by atomic
mass. - Henry Moseley rearranged the periodic table to be
in order of increasing atomic number. The
current periodic table is still arranged by
atomic number (number of protons).
10
Periodic Table
- Parts
- Rows are known as periods. Think about how we
write, left to right, and that we add periods to
the end of our sentences. - Columns are known as families or groups.
Elements in the same group have similar
characteristics.
11
Metals
- Metals
- Metals are elements that are generally shiny,
hard, ductile, malleable, and good conductors of
electricity. - Malleable capable of being pounded into shapes
- Ductile capable of being drawn into wires
- Conductor allows heat and electricity to flow
through it - Metals are located to the left of the zig-zag
line on the periodic table.
12
Non-Metals and Metalloids
- Non-metals
- Non-metals are elements that have properties
opposite to those of metals. - Non-metals are located to the right of the
zig-zag line on the periodic table. - Metalloids
- Metalloids have properties in common with both
metals and and non-metals. - Metalloids are located along the zig-zag line on
the periodic table.
13
Chemical Vs Physical
- Chemical versus Physical Changes
- 1) A physical change is a change that does NOT
involve a change in the chemical makeup of a
substance. - Example Ice melting to water. It is H2O before
and it is H2O afterwards. - H2O (ice) ? H2O (water)
- 2) A chemical change is a change that does
involve a change in the chemical makeup of a
substance. - Example Water being broken down into hydrogen
and oxygen. - 2H2O ? 2H2 O2
14
Synthesis and Decomposition
- 3) A synthesis reaction involves 2 or more parts
coming together to make 1 thing. - 2H2 O2 ? 2H2O
- 4) A decomposition reaction involves 1 things
breaking down into 2 or more parts. - 2H2O ? 2H2 O2
15
Chemical Versus Physical
- Ex) What kind of reaction involves the breakdown
of 1 thing into 2. - Ex) What kind of reaction involves 2 things being
made into 1. - Ex) What kind of change involves a change on the
chemical level? - Ex) What kind of change does NOT involve a change
on the chemical level?
16
Acids and Bases
- Acids and Bases
- 1) An acid is a substance that makes H ions in
solution. - An example of an acid is orange juice.
- Acids taste sour.
- 2) A base is a substance that makes OH- ions in
solution. - An example of a base is laundry detergent.
- Bases taste bitter.
- 3) A neutral solution is not an acid or a base.
- Water is neutral.
17
Acids and Bases
- Ex) A solution was found to be sour in taste.
What kind of ions does this solution make? - Ex) A solution was found to be bitter in taste.
What kind of ions does this solution make? - Ex) A solution does not have H or OH- ions.
What can we call this solution? - Ex) Is orange juice an acid or base?
18
Indicators
- Indicators change color in the presence of acids
and bases. - Cabbage juice can be used as an indicator.
- Red/pink acid
- Blue/green Base
- Purple Neutral
19
Indicator
- For each of the following colors, tell whether it
is an acid, base, or neutral. - Ex) Pink
- Ex) Blue
- Ex) Green
- Ex) Purple
20
Simple Machines
- There are 6 simple machines
- Wedge
- Wheel and Axle
- Lever
- Pulley
- Inclined Plane
- Screw
21
Simple Machines
22
Simple Machines
- Ex) An inclined plane wrapped around a pole is
similar to what simple machine? - Ex) What simple machine is like a ramp?
- Ex) What simple machine would be good for lifting
a box to a second story window?
23
Newton's Laws of Motion
- Newton had 3 laws of motion.
- 1st Law An object in motion or rest stays in
motion or rest until a force acts on it. - 2nd Law Force equals mass times acceleration
- 3rd Law For every action there is an equal and
opposite reaction.
24
(No Transcript)