Earned Value Management - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Earned Value Management
Description:
Only 2 tasks; both overspent. We had planned to do 3 of work, but only earned' 2. ... fails quality testing, and has to be reworked in Month 5, meaning that none of ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:428
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Earned Value Management
1
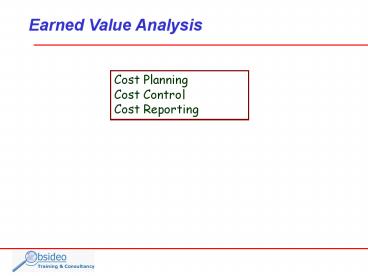
Earned Value Analysis
Cost Planning Cost Control Cost Reporting
2
Earned Value Analysis
the original plan
BAC Budget At Completion 5
EV 2
Only 2 tasks both overspent. We had planned to
do 3 of work, but only earned
2. Unfortunately it cost us 4 to do it. We can
use the power of EVA to forecast the future
3
Earned Value Analysis
If you, in the role of project manager, convince
your customer that the project will cost xxx, and
you also cost each task or major milestone along
the way, then in the customers mind each task or
milestone will be worth what you said.
So if you are so poor at controlling the project
that a task has cost you twice the original
estimate why should the customer pay for your
incompetence?
This is the essence of EVA you will only earn
what the customer sees as the value of task. Many
large organisations pay their contractors in this
way
4
Earned Value Analysis Jargon - 1
EV is Earned Value
EV 2
PV is Planned Value
PV 3
AC is Actual Cost
AC 4
Earned Value means the total value of the tasks
we have actually completed by this time
Planned Value means the total value of the tasks
we had meant to complete by this time
Actual Cost means the total cost we have incurred
getting to this point in time
5
So What? 1
IF
?
?
?
?
6
The Graphs
cost
PV
The Actual Cost is running ahead of the Planned
Value, therefore the project is over budget
The Earned Value is running behind Planned Value,
therefore the project is behind schedule
time
7
Earned Value Analysis Jargon - 2
We can look at variance
A negative variance is BAD
8
Earned Value Analysis Jargon - 3
We can extrapolate from the current position.
Everything we do seems to cost us twice what we
had planned
9
So What? - 2
This is only true if all future tasks overrun at
the same rate as now. If we think we have fixed
the problems behind the current cost overrun then
a better EAC formula is
This is a much smaller EAC, but remember our
premise
10
Earned Value Analysis Jargon - 4
The EAC is obviously a really important figure in
the overall cost control for the project, but
there is another figure that many people will
want to know
ETC is Estimate to Complete, meaning how much
more money will it take to finish this project.
ETC is easy to compute.
11
Earned Value Analysis Jargon - 5
More extrapolation, albeit slightly more risky.
We know that every task we have finished seems to
be taking longer than planned, so maybe we can
infer that all future tasks will overrun their
schedule by a similar amount. This means we can
calculate a Schedule Performance Index, as
follows
So if the original duration was 5, the new
duration could be OD/SPI 5/0.66 7.6
12
Earned Value Analysis
- EVA can be a powerful tool for forecasting
outturn - it requires accurate estimating as well as
control - It assumes future cost performance will be
similar to current
Upper Control Limit
Lower Control Limit
13
Classroom Practice - 1
All figures are cumulative
1. What is the CPI at the end of month 4
2. What is the SPI at the end of month 4
3. What is the EAC at the end of month 4
4. What is the ETC at the end of month 4
14
Classroom Practice - 2
All figures are cumulative
1. What is the CV at the end of month 4
2. What is the SV at the end of month 4
3. If all the work completed in Month 4 fails
quality testing, and has to be reworked in Month
5, meaning that none of Month 5s tasks can be
completed
3a. What is the EV at the end of month 5
3b. What is the AC at the end of month 5
3c. What is the CPI at the end of month 5