5. Universal Laws of Motion - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 31
Title:
5. Universal Laws of Motion
Description:
Moon Rise/Set by Phase. The different phases also rise and set at ... Note: the moon spends as much time in the sky in ... on the phase of the Moon. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:243
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 5. Universal Laws of Motion
1
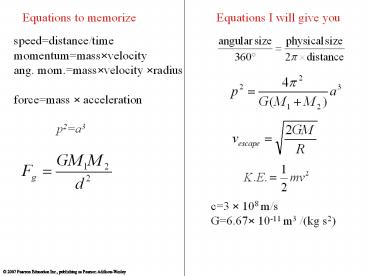
Equations to memorize
Equations I will give you
speeddistance/time momentummass?velocity ang.
mom.mass?velocity ?radius forcemass ? acceler
ation
p2a3
c3 ? 108 m/s G6.67? 10-11 m3 /(kg s2)
2
Moon Rise/Set by Phase
The different phases also rise and set at
different times At full moon, the moon is opposi
te the sun, so it rises at sunset, culminates at
midnight, and sets at dawn At new moon, the moon
is on the same side as the sun, and so is only in
the sky during the day (rises at dawn, sets at
dusk) First quarter rises at noon, culminates at
6pm, and sets at midnight Last quarter rises at m
idnight, culminates at 6am, and sets at noon
Note the moon spends as much time in the sky in
daytime as at night!
3
Moon Rise/Set by Phase
Time the Moon Rises and Sets for Different Phases
4
(No Transcript)
5
- Now lets step through the Universe in powers of
10
Zooming Out or Zooming In 26 Orders of Magnitude
6
(No Transcript)
7
Tides and Phases
Size of tides depends on the phase of the Moon.
Note spring tides means extreme high and low tides
Tides
http//maps.google.com/maps?hlenieUTF8ll51.64
359,-2.622986spn0.755036,1.779785tpz9
http//www.youtube.com/watch?vPtUmLLlm7S0feature
related
8
(No Transcript)
9
The sky varies with latitude but not longitude.
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
What causes the seasons?
Seasons depend on how Earths axis affects the
directness of sunlight. Note - not because one he
misphere is closer to the sun!!!
13
Axis tilt changes directness of sunlight during
the year.
Why Does Flux Sunlight Vary
14
(No Transcript)
15
Keplers Third Law
Kepler's 3rd Law
16
100 billion stars
17
Where do we sit?
18
How did we come to be?
19
Are we ever sitting still?
Earth rotates on axis 1,000 km/hr
Earth orbits Sun 100,000 km/hr
Solar system moves among stars 70,000 km/hr
Milky Way rotates 800,000 km/hr
Milky Way moves in Local Group
Universe expands
20
100 billion stars
Momentumm?v
Ang Momentumm?v?r
21
p2a3
22
100,000 ly diameter
23
in 1 second it accelerates 10 m/s
after 5 seconds it is at 50 m/s
The change of mass has no effect
in m, s, kg
in A.U., years, Solar masses
See over
24
1parsec 3.26ly 206,265 AU
1arcsec1/60/60 degrees 2.78?10-4 degrees
25
Angular Size
An objects angular size appears smaller if it is
farther away.
26
We see apparent retrograde motion when we pass by
a planet in its orbit.
Mars Retrograde Motion
27
- How did Copernicus, Tycho, and Kepler challenge
the Earth-centered idea? - Copernicus created a Sun-centered model Tycho
provided the data needed to improve this model
Kepler found a model that fit Tychos data. - Keplers three laws of planetary motion
- 1. The orbit of each planet is an ellipse with
the Sun at one focus. - 2. As a planet moves around its orbit it sweeps
our equal areas in equal times. - 3. More distant planets orbit the Sun at slower
average speeds p2 a3. - Galileo solidified the Copernican revolution.
- His experiments and observations overcame the
remaining objections to the Sun-centered solar
system.
28
- Newtons Three Laws of Motion
- An object moves at constant velocity if no net
force is acting. - Force mass ? acceleration.
- For every force, there is an equal and opposite
reaction force.
29
Conservation Laws
- Conservation of momentum
- Conservation of angular momentum
- Conservation of energy
30
You are an astronomer on planet Nearth, which
orbits a distant star. It has recently been
accepted that Nearth is spherical in shape,
though no one knows its size. One day, while
studying in the library of Alectown, you learn
that on the equinox your sun is directly overhead
in the city of Nyene, located 1300 due north of
you. On the equinox, you go outside in Alectown
and observe that the altitude of your sun is 81
.
Measurements Nyene to Alectown distance 130
0km angle difference 90- 81 angle differen
ce 9 CN 9/360 1300 CN 1300 36
0/9 52000 5.2 ? 104
31
Equations to memorize
Equations I will give you
speeddistance/time momentummass?velocity ang.
mom.mass?velocity ?radius forcemass ? acceler
ation
p2a3
c3 ? 108 m/s G6.67? 10-11 m3 /(kg s2)