T' cruzi facts lifecycle continued
1 / 10
Title:
T' cruzi facts lifecycle continued
Description:
visceral / connective tissue involvement (unique to Chagas) ... visceral: megaesophagus, megacolon. cardiac muscle: cardiac dilation, multiple carditis failure ... –
Number of Views:82
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: T' cruzi facts lifecycle continued
1
(No Transcript)
2
T. cruzi facts / life-cycle continued
- T. cruzi is transmitted via the feces of the
triatomid bug which is introduced when the insect
bites (he likes to defacate while he feeds
nobody has asked him why). The DH rubs the
painful bite thereby rubbing the bug feces (if
present) into the wound. Bites are most common
around the facial area, hence the name kissing
bug. Triatomid feces can also be introduced in
an already present wound and into the conjunctiva
of the eye. Transmission also occurs via blood
transfusion and perinatally. There are 2 disease
causing troph stages of T. cruzi a) the
tryp(an)omastigote which is found in blood, and
the b) amastigote (leishmanial form) which is
present in advanced chronic cases, and is found
in visceral connective tissues
reticuloendothelial, cardiac, brain. Amastigotes
divide asexually intracellularly (often in
macrophages) to become trypomastigotes.
3
- T. cruzi
- disease (South) American trypanosomiasis,
Chagas - intermediate host triatomid or reduviid bug
- usually bites on the face also called
kissing bug - definitive host humans
- house pets, rodents, wild animals
4
T. cruzi life-cycle
5
Focus on pathogens Trypanosomes
- T. cruzi Epidemiology
- found in southern U.S. - C. America - all of S.
America. - 16-18 million currently infected, half of these
in Brazil. - 50 million at risk 50,000 annual deaths
- most cases are children
- US cases are rarely endemic? Travel? Imports?
- many years (?) following the initial acute
symptoms, 10-30 of patients develop the advanced
chronic symptoms latency? - much more treatable (or treated?) than T. brucei
lower mortality. This is at least true of the
acute phase.
6
Focus on pathogens Trypanosomes
- T. cruzi pathology / clinical symptoms
- swollen knot (chagoma) at site of bug bite /
feces introduction - painless edema of perioccular tissues
- recurring fever
- lymphodenopathy
- edema of lower extremities
- advanced chronic symptoms
- visceral / connective tissue involvement (unique
to Chagas) - reticuloendothelial intra-macrophage
amastigotes - visceral megaesophagus, megacolon
- cardiac muscle cardiac dilation, multiple
carditis ? failure - brain tissue meningoencephalitis ? coma ? death
7
(No Transcript)
8
Focus on pathogens Trypanosomes
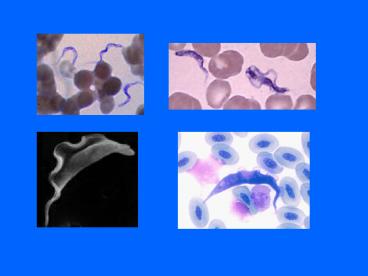
- T. cruzi Laboratory diagnosis of trophs
- Tryp(an)omastigote
- sample blood
- C-shaped troph with classic trypanosome morph
(see - description on T. brucei laboratory
diagnosis slide?) - 15-20uM long 1-3uM wide
- Amastigote
- sample blood, biopsy
- will be seen intracelluarly intra-macrophage
parasites - round-oval, 2-4uM in size
- lacks a prominent flagellum
9
T. cruzi trypomastigotes
10
T. cruzi amastigotes