Subtropical High-pressure Cells - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Subtropical High-pressure Cells
Description:
... low pressure systems exist in some locations, they not only impact local weather ... Teleconnections: relationship between weather or climate patterns at ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:117
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Subtropical High-pressure Cells
1
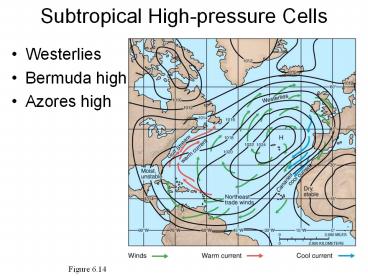
Subtropical High-pressure Cells
- Westerlies
- Bermuda high
- Azores high
Figure 6.14
2
Rossby Waves
- Great waving undulations within the westerlies
flow of geostrophic winds. - Instrumental to the latitudinal transportation
of energy. - Play an important role in determining divergence
and convergence areas of the upper atmosphere.
3
Upper Atmospheric Circulation
- Rossby waves
- Jet stream
4
Rossby Waves
Figure 6.17
5
Rossby Waves
Figure 6.17
6
Constant Isobaric Surface
Figure 6.16
7
Jet Stream
8
Jet Streams
Figure 6.18
9
The Polar Front and Jet Streams
- Strong boundaries often occur between warm and
cold air. In the mid-latitudes, the polar front
marks this thermal discontinuity at the surface.
10
(No Transcript)
11
Multiyear Oscillations
- North Atlantic Oscillation
- Believed to regulate hurricane activity
- Pacific Decadal Oscillation
- Operates on 20-30 year cycles
- Now known to heavily influence climate and
wildfire activity
12
North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO)
- A large scale seesaw in atmospheric mass between
the subtropical high and the polar low. - Positive NAO versus negative NAO
13
Arctic Oscillation (AO)
- Opposing atmospheric pressure patterns in
northern middle and high latitudes. Warm phase
versus cold phase.
14
Pacific Decadal Oscillation
15
Local Winds
- Land-sea breezes
- Mountain-valley breezes
- Katabatic winds
- Monsoon patterns
16
Land-Sea Breezes
Figure 6.19
17
Mountain-Valley breezes
Figure 6.20
18
Katabatic winds
19
Chinook Santa Ana Winds
- Winds that flow down the lee side of mountain
ranges
20
Monsoonal Winds
Figure 6.21
21
Oceanic Currents
- Surface Currents
- Cold high latitude
- Warm low latitude
- Gyres circulate in which directions?
22
Major Ocean Currents
Peru Current
Figure 6.22
23
Oceanic Currents
- Deep Currents
- Thermohaline circulation
- Distributes energy
- Effects of global warming?
24
Deep Currents
Figure 6.23
25
ENSO events
- ENSO events are a disruption of the
ocean-atmosphere system in the tropical Pacific - El Nino Southern Oscillation
- El Nino ocean
- Southern Oscillation atmosphere
- How are they reconstructed?
26
El Niño
- Changes in pressure patterns
- Changes in wind patterns
- Mainly concentrated in the Pacific Ocean
- Measured using Southern Oscillation Index
- Differences in pressure observed in Tahiti and
Darwin, Australia - Combined to form ENSO
- Affects weather globally
27
Buoys
28
El Niño
29
Impacts of ENSO Events
- Marine environments
- Atlantic hurricanes
- Global precipitation patterns
- Wildfires
30
- Australia-Drought and bush fires
- Indonesia, Philippines-Crops fail, starvation
follows - India, Sri Lanka-Drought,fresh water shortages
- Tahiti-6 tropical cyclones
- South America-Fish industry devastated
- Across the Pacific-Coral reefs die
- Colorado River basin-Flooding, mud slides
- Gulf states-Downpours cause death, property
damage - Peru, Ecuador-Floods, landslides
- Southern Africa-Drought, disease, malnutrition
31
El Niño
32
ENSO
- When high and low pressure systems exist in some
locations, they not only impact local weather
conditions, but also influence the overall size,
shape, and position of the entire Rossby wave
pattern - Teleconnections relationship between weather or
climate patterns at two widely separated locations
33
ENSO
34
ENSO
- Occurs once every 3 to 5 years (but varies)
- Is regulated by (what else) PDO
- Switch to PDO warm phase in 1999 appears to have
dampened ENSO - Major ENSO events in last 25 years 19821983,
19861987, 19911993, 19971998, 20022003 - 19971998 was so intense, it disrupted global
weather
35
Normal
36
Normal Year
37
ENSO
38
ENSO
39
ENSO Year
40
La Nina
- El Niño warm phase, La Niña cool phase
- La Niña brings extreme normal conditions
- Not all El Niño events are followed by La Niña
events - La Niña events increase wildfires in the SE and
Atlantic hurricanes
41
La Nina