OSI and Network Devices - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title:
OSI and Network Devices
Description:
Make decisions about where to direct them based on each frame's MAC address ... Link state algorithm; based on hop count and weighted area for congestion ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:49
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: OSI and Network Devices
1
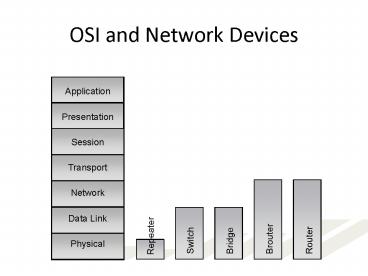
OSI and Network Devices
Application Presentation Session Transport Network
Data Link Physical
2
Repeaters
- Connectivity device that regenerates and
amplifies an analog or digital signal
Repeater
3
Repeaters
- Repeaters simplest type of connectivity devices
that regenerate a digital signal - Operate in Physical layer
- Cannot improve or correct bad or erroneous signal
- Regenerate signal over entire segment
- One input port and one output port
- Suited only to bus topology networks
4
Repeater Operation
repeater
5
Hub repeater with more than one output port
- Multiple data ports
- Operate at Physical layer
- Uplink port allows connection to another hub or
other connectivity device - On Ethernet networks, can serve as central
connection point of star or star-based hybrid
topology - On Token Ring networks, hubs are called
Multistation Access Units (MAUs)
6
Hubs
- Multiport repeater containing one port that
connects to a networks backbone and multiple
ports that connect to a group of workstations
Detailed diagram of a hub
7
Hubs
- 3COM SuperStack 3 Baseline 24 port 10/100 Hub
- 373.99 (5 port 77.99)
8
Hubs
- Passive hubs
- Only repeats signal
- Active hubs
- Regenerates signal
- Intelligent hubs
- Possesses processing capabilities
- SNMP
9
Hubs in a network design
10
Standalone Hubs
- Serves a workgroup of computers that are
separated from the rest of the network
Standalone hubs
11
Stackable Hubs
- Designed to be linked with other hubs in a single
telecommunications closet
Rack-mounted stackable hubs
Stackable hubs
12
Modular Hubs andIntelligent Hubs
- Modular hub
- Provide a number of interface options within one
chassis - Intelligent hubs
- Also called managed hubs
- MIB (management information base)
- Collection of data used by management programs to
analyze network performance
13
Installing a Hub
- As with NICs, the best way to ensure a hub is
properly installed is to follow the
manufacturers guidelines
Connecting a workstation to a hub
14
Choosing the Right Hub
- Performance
- Cost
- Size and growth
- Security
- Management benefits
- Reliability
15
Bridges
- Like a repeater, it has a single input and single
output port - Unlike a repeater, it can interpret the data it
retransmits - FibreBridge 1100D - Bridge 1,879.99 (1000Mbs)
Bridge
16
Bridge Operation
- Connect two network segments
- Analyze incoming frames
- Make decisions about where to direct them based
on each frames MAC address - Operate at Data Link layer
- Protocol independent
- Can move data more rapidly than traditional
routers - Extend Ethernet network without extending
collision domain or segment - Can be programmed to filter out certain types of
frames
17
Bridges
- Filtering database
- Collection of data created and used by a bridge
that correlates the MAC addresses of connected
workstations with their locations - Also known as a forwarding table
FIGURE 6-22 Bridges use of a filtering database
18
Bridges
- Transparent Bridging
- Method used on most Ethernet networks
- Source Route Bridging
- Method used on most Token Ring networks
- Translation Bridging
- Method that can connect Token Ring and Ethernet
networks
19
Bridge Operation
Data Link layer
bridge
20
Switches
- Switches subdivide a network into smaller logical
pieces - Collision domain
- Portion of a LAN encompassing devices that may
cause and detect collisions among their group
Example of LAN switches
21
Swtiches
- Subdivide network into smaller logical pieces
(segments) - Layer 2 standard switch
- Layer 3 router switch
- Layer 4 application switch
- Acts as multiport bridges
- Most have internal processor, OS, memory, and
several ports - Each port on switch acts like bridge
- Each connected device effectively receives own
dedicated channel
22
Routing Switches
- Routing switch
- Another term for a Layer 3 and sometimes a Layer
4 switch - Hewlett-Packard Procurve routing switch 9308M
- 10/100/Gigabit managed modular switch with 8 open
module slots for up to 64 Gigabit or 168 10/100
ports or any combination - 13,179.88
23
Switch
- Cisco Catalyst 2924M 24 port 10/100 Switch
- 1,599.99
24
Cut-Through Mode andStore and Forward Mode
- Cut-through mode
- Switching mode in which switch reads a frames
header and decides where to forward the data
before it receives the entire packet - Advantage is speed
- Can detect runts, or packet fragments
- Store and forward mode
- Switching mode in which switch reads the entire
data frame into its memory and checks it for
accuracy before transmitting it - Transmits data more accurately
- Slower than cut-through mode
- Can transfer data between segments running
different transmission speeds
25
Creating VLANs with Switches
- Virtual LANs (VLANs) logically separate networks
within networks - Use switches to group a number of ports into a
broadcast domain - Combination of ports making up a Layer 2 segment
- In TCP/IP, referred to as a subnet
- VLANs created by properly configuring switchs
software - VLAN configuration requires careful planning
26
Using Switches to Create VLANs
- Virtual local area networks (VLANs)
- Means by which a switch can logically group a
number of ports into a broadcast domain - Broadcast domain
- Combination of ports that make up a Layer 2
segment and must be connected to a Layer 3 device
Simple VLAN design
27
Higher-Layer Switches
- Switch capable of interpreting Layer 3 is called
a Layer 3 switch or routing switches - Switch capable of interpreting Layer 4 is called
a Layer 4 switch or application switches - Ability to interpret higher-layer data enables
switches to perform advanced filtering,
statistics keeping, and security functions
28
Routers
- Multiport device
- Can connect integrate LANs and WANs running at
different transmission speeds and using a variety
of protocols - Multiport connectivity devices that direct data
between nodes on a network - Operate at Network layer
- Reads incoming packets logical addressing
information - Determines where to deliver packet
- Determines shortest path to that network
- Protocol-dependent
29
Router Features and Functions
- Modular router
- Router with multiple slots that can hold
different interface cards or other devices
Typical routers Cisco 3661 - 8,149.99
30
Router Features and Functions
- Filter out broadcast transmission to alleviate
network congestion - Determine the best path for data to follow
- Reroute traffic
- Prevent certain types of traffic from getting to
a network - Support simultaneous local and remote activity
- Provide high network fault tolerance through
redundant components - Monitor network traffic and report statistics to
a MIB - Diagnose internal or other connectivity problems
and trigger alarms - Support simultaneous local and remote connectivity
31
Router Operation
Network layer
Data Link layer
router
32
Routers
Placement of routers on a LAN
33
Routing Protocols
- Means by which routers communicate with each
other about network status - Convergence time
- The time it takes for a router to recognize a
best path in the event of a change or outage - Bandwidth overhead
- Burden placed on an underlying network to support
the routing protocol
34
Router Features and Functions
- Interior router directs data between nodes on
autonomous LANs - Exterior router directs data between nodes
external to given autonomous LAN - Border routers connect autonomous LAN with a WAN
- Static routing network administrator programs
router to use specific paths between nodes - Dynamic routing automatically calculates best
path between two nodes - Accumulates information in routing table
35
Routing Protocols
- Locates the best path. Best path refers to the
most efficient route from one node on a network
to another - RIP (Routing Information Protocol) for IP and IPX
- Distance vector algorithm based on hop count
- Small networks with fewer than 15 routers
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) for IP
- Link state algorithm based on hop count and
weighted area for congestion - EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
Protocol) for IP, IPX, and AppleTalk - BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) for IP
- Internet
36
Brouters - Bridge router
- Industry term used to describe routers that take
on some characteristics of bridges - Can forward non-routable protocols
- Connect multiple network types through one device
- Cisco 1600 1604
- Bridge/router 1,249.99
37
Gateways
- Combination of networking hardware and software
that connects two dissimilar kinds of networks
using different formatting, communications
protocols, or architecture - Repackage information to be read by another
system - Operates at multiple OSI Model layers
- E-mail gateway
- IBM host gateway
- Internet gateway
- LAN gateway
- Proxy server does processing on each data packet
at the application level
38
Gateway
- CISCO PIX Firewall Gateway
- 3,649.99
- 256,000 connections
- 170 megabits per second (Mbps)