Initial Results from the SPMMRC 7T MRI Scanner
1 / 1
Title:
Initial Results from the SPMMRC 7T MRI Scanner
Description:
P Wright, W Van Der Zwaag, A Peters, R Coxon, S Francis, P ... optimisation is ... with the aim of optimising imaging sequences on the 7T ... –
Number of Views:116
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Initial Results from the SPMMRC 7T MRI Scanner
1
Initial Results from the SPMMRC 7T MRI Scanner
P Wright, W Van Der Zwaag, A Peters, R Coxon, S
Francis, P Glover, P Gowland, R Bowtell and P
Morris 1Sir Peter Mansfield Magnetic Resonance
Centre, University of Nottingham, University
Park, Nottingham
Introduction
- With the growing acceptance of 3.0T magnetic
resonance (MR) scanners in the clinical setting,
research is turning to ultra-high field MRI. - The new Philips 7T MR scanner allows the
University of Nottingham to remain at the
forefront of MR research. - Ultra-high field gives increased signal to noise
ratio leading to increased contrast in BOLD
imaging, increased perfusion sensitivity and
access to novel image contrast mechanisms. - Technical problems associated with imaging at
ultra high field, including image inhomogeneity
and magnetic field distortion are now being
tackled in partnership with the manufacturer,
with the aim of optimising imaging sequences on
the 7T scanner. - Motivations behind establishing a 7T facility
include implementation of single trial fMRI to
study learning and adaptation as well as gaining
access to anatomical information of exceptional
detail within a reasonable acquisition time.
Results
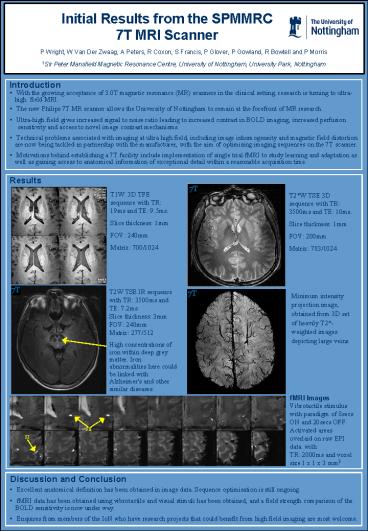
T1W 3D TFE sequence with TR 19ms and TE
9.5ms. Slice thickness 1mm FOV 240mm Matrix
700/1024
T2W TSE 3D sequence with TR 3500ms and TE
10ms. Slice thickness 1mm FOV 200mm Matrix
783/1024
T2W TSE IR sequence with TR 3500ms and TE
7.2msSlice thickness 3mmFOV 240mmMatrix
277/512
Minimum intensity projection image, obtained from
3D set of heavily T2-weighted images depicting
large veins.
High concentrations of iron within deep grey
matter. Iron abnormalities here could be linked
with Alzheimer's and other similar diseases.
fMRI Images
Vibrotactile stimulus with paradigm of 8secs ON
and 20secs OFF. Activated areas overlaid on raw
EPI data with TR 2000ms and voxel size 1 x 1 x
3 mm3
SII
SI
Discussion and Conclusion
- Excellent anatomical definition has been
obtained in image data. Sequence optimisation is
still ongoing. - fMRI data has been obtained using vibrotactile
and visual stimuli has been obtained, and a field
strength comparison of the BOLD sensitivity is
now under way. - Enquires from members of the IoN who have
research projects that could benefit from high
field imaging are most welcome.