REFINED DYNAMIC STALL MODEL FOR THE S809 AEROFOIL - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 45
Title: REFINED DYNAMIC STALL MODEL FOR THE S809 AEROFOIL
1
(No Transcript)
2
(No Transcript)
3
NACA 0012
Legend 1 Beddoes original 3rd generation
dynamic stall model 2 Leishmans modification in
reattachment
4
Comparison of unsteady airloads
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
(a)
(b)
- Pitch rates (NACA 0015)
- Staring angles (NACA 23012C)
- Aerofoils (NACA series)
(c)
8
(No Transcript)
9
Normal force reconstructions for ramp-down (Niven
et al)
Prediction with the Beddoes original model The
improved prediction
10
Comparison of unsteady airloads
11
(a)
(b)
- Pitch rates (NACA 0015)
- Staring angles (NACA 23012C)
- Aerofoils (NACA series)
(c)
12
Pressure distributions for a ramp-down test of
the NACA 23012B (Green et al)
13
(No Transcript)
14
Onset criterion
15
Force reconstructions for NACA0012 ramp-up test
(r 0.0145)
16
Force reconstructions for S809 ramp-up test (r
0.0169)
17
NORMAL FORCE
PRESSURE COEFFICIENT AT 2.5 CHORD
18
Non-dimensional time delay constants for
reattachment processby Green et al
19
?min0 Tr ?
20
Linear fits for ?min
21
Reconstructions for normal force
(a) r -0.005 (b) r -0.0119
NACA 0015, ramp-down
22
CN reconstruction with different gradients during
the down-stroke for NACA0012 (oscillation, ?
0.075)
23
NACA 23012B
? 0.076 ?0.101 Legend 1 Beddoes original
3rd generation dynamic stall model 2 Beddoess
return and Sheng et als onset criterion
21 3 Leishmans return and Sheng et als onset
criterion 4 New return and Sheng et als onset
criterion
24
Force reconstructions for NACA0012 oscillatory
test (? 0.124 )
25
Force reconstructions for S809 oscillatory test
(? 0.074 )
26
(No Transcript)
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
Forced transition model
30
Comparison clean vs. sanded
Ramp-up test
Static case
31
continued
32
clean vs. sanded (continued)
33
Ramp-up cases (r0.0098)
34
Ramp-up cases (r0.0253)
35
Oscillatory cases (?0.01)
36
Oscillatory cases (?0.05)
37
Oscillatory cases (?0.15)
38
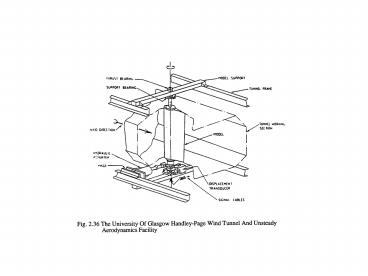
Glasgow University Rotor Aeromechanics
Laboratory Wind Turbine Aerodynamic Modelling
39
Vorticity Transport Model (VTM)
- High fidelity wake modelling
- Solves vorticity transport equation gt
- Accurate wake structure and evolution by explicit
conservation of vorticity and control using flux
limiters - Efficient Weissinger-L lifting line blade
aerodynamic model - Rigid-blade dynamics modelled using a Lagrangian
formulation - Validated extensively for rotorcraft
applications - (Brown 2000, Brown et al. 2005 AIAA Journal)
40
Turbine Wake Interaction using VTM
Contours of vorticity magnitude represent
wake Blue Rotor 1 Yellow Rotor 2 (downwind)
- Two 3-bladed turbines
- Operating in yawed crosswind conditions
- Tip speed ratio 4
- Constant pitch
- Constant rotor speed
41
Turbine Lifting Performance Degradation
Wind direction
42
CHRONoS
- Compressible High Resolution Overset Navier
Stokes Solver - Cell-vertex finite volume solver
- Structured overset meshes
- RANS turbulence modelling Spalart Allmaras
model - LES modelling Detached Eddy Simulation and wall
modelled LES - Steady / unsteady calculations, moving meshes,
deforming meshes - Extensively validated for rotor flows
performance, vortex evolution, dynamic stall,
blade vortex interaction etc.
43
Flow Field in the Vicinity of a Blade Tip using
CHRONoS
Streamwise vorticity contours
44
(No Transcript)
45
(No Transcript)