Compact Discs - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
Compact Discs
Description:
To read this information, the CD player passes a laser beam over the track. ... the beam passes over a bump, the light is bounced away from the optical sensor. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:58
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Compact Discs
1
Compact Discs
2
Track Characteristics
3
CDRom Bumps
4
CDRom Bumps etc.
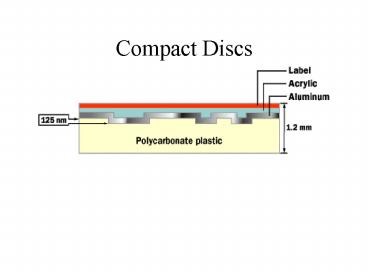
- To read this information, the CD player passes a
laser beam over the track. When the laser passes
over a flat area in the track, the beam is
reflected directly to an optical sensor on the
laser assembly. The CD player interprets this as
a 1. When the beam passes over a bump, the light
is bounced away from the optical sensor. The CD
player recognizes this as a 0. - http//static.howstuffworks.com/flash/cd-read.swf
5
CD-R
- A CD-R doesn't have the same bumps and lands as a
conventional CD. Instead, the disc has a dye
layer underneath a smooth, reflective surface. On
a blank CD-R disc, the dye layer is completely
translucent, so all light reflects. The write
laser darkens the spots where the bumps would be
in a conventional CD, forming non-reflecting
areas. - http//static.howstuffworks.com/flash/cd-burner-cd
r.swf
6
DVD The Basics
DVD is very similar to a CD, but it has a much
larger data capacity. A standard DVD holds about
? times more data than a CD does. This huge
capacity means that a DVD has enough room to
store a ? movie, as well as a lot of other
information.
7
The DVD Player
A DVD player is very similar to a CD player. It
has a laser assembly that shines the laser beam
onto the surface of the disc to read the pattern
of bumps. The DVD player decodes the MPEG-2
encoded movie, turning it into a standard
composite video signal. The player also decodes
the audio stream and sends it to a Dolby decoder,
where it is amplified and sent to the speakers.
8
DVD Media
- DVD-ROM can
- DVD-R can
- DVDR can
- DVDRW can
9
DVD Capacities
10
DVD Structure
11
The DVD Video Format
Even though its storage capacity is huge, the
uncompressed video data of a full-length movie
would never fit on a DVD. In order to fit a movie
on a DVD, you need video compression. A group
called the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG)
establishes the standards for compressing moving
pictures
12
CODECs
A CODEC Audio and Video Codecs Lossy or
Lossless Codecs designed around content Sport
codec for ? Art codec for ? Audio Codecs Mobile
phones - ? Music ?
13
CODECs
- Multimedia codecs
- Both audio and video
- Need to be ?
- so 3rd channel contains ?
- 1000s of codecs
- Compatibility and obsolescence issues
- Not true of raw PCM data ?
14
CODECs
RealVideo RealNetworks RealMedia (.RM)
file Streaming video live TV WMV Windows
Media Video (competition to Real) Microsoft ?
applications Used in ?
technology DivX video codec Compress video
into relatively small file sizes Still maintains
visual quality Lossy MPEG-4 compression - used
for ripping
15
DVD/CD Feature
Fill with N/A, R or W/R in your own time
16
Blu-ray
- High density ? disc
- ? laser used to read/write - 405nm
- more on disc than ? laser 650nm
- 2-layer disc ?GB (6x DVD)
- Competition was HD DVD format
- 2/08 Toshiba withdrew HD DVD design
- Xbox 360 blu-ray?
17
Blu-ray
- Future?
- Quad-layer ( ?GB) demonstrated
- ? hours ?Mbit/s (HDTV) video
- ? hours video Cinema 4K format
- (4k horizontal pixel resolution 40962160)
- ?GB possible using ?, ?GB layers