Molecular Dynamics: Introduction - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Molecular Dynamics: Introduction
Description:
How do we describe the potential energy V(x) for a. molecule? ... Equation for non-bonded terms in P.E. Molecular Dynamics: Introduction ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:160
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Molecular Dynamics: Introduction
1
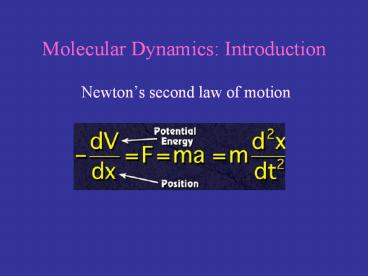
Molecular Dynamics Introduction
- Newtons second law of motion
2
Molecular Dynamics Introduction
- We need to know
- The motion of the
- atoms in a molecule, x(t)
- and therefore,
- the potential energy, V(x)
3
Molecular Dynamics Introduction
- How do we describe the potential energy V(x) for
a - molecule?
- Potential Energy includes terms for
- Bond stretching
- Angle Bending
- Torsional rotation
- Improper dihedrals
4
Molecular Dynamics Introduction
- Potential energy includes terms for (contd.)
- Electrostatic
- Interactions
- van der Waals
- Interactions
5
Molecular Dynamics Introduction
- Equation for covalent terms in P.E.
6
Molecular Dynamics Introduction
- Equation for non-bonded terms in P.E.
7
Molecular Dynamics Introduction
- Each of these interactions exerts a force onto a
given atom of the molecule - The total resulting force on each atom is
calculated using the PE function
Knowing the force on an atom, its movement due to
the force is then calculated
8
Molecular Dynamics Introduction
- To do this, we should know
- at given time t,
- initial position of the atom
- x1
- its velocity
- v1 dx1/dt
- and the acceleration
- a1 d2x1/dt2 m-1F(x1)
9
Molecular Dynamics Introduction
- The position x2 , of the atom after time interval
?t would be, - and the velocity v2 would be,
10
How a molecule changes during MD
11
Molecular Dynamics Introduction
- In general, given the values x1, v1 and the
potential energy V(x), the molecular trajectory
x(t) can be calculated, using,
12
DOCKING
13
DOCKING