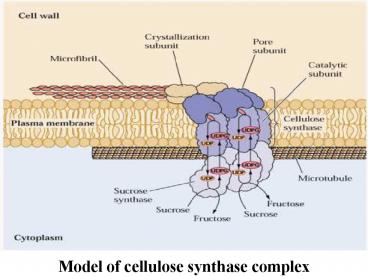
Model of cellulose synthase complex - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 41
Title:
Model of cellulose synthase complex
Description:
Xylem and phloem transport streams can be sampled by several methods ... Important sites of xylem-to-phloem solute transfer occur at leaf traces and in ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1779
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Model of cellulose synthase complex
1
Model of cellulose synthase complex
2
(A) Diagram of the membrane organization of a
plant mitochondrion. (B) Thin-section electron
micrograph of a plant mitochondrion
3
The general mechanism of oxidative
phosphorylation in mitochondria
4
Organization of the plant mitochondrial electron
transfer chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane
5
Generalized scheme for the three pathways of
decarboxylation in the bundle sheath cells of C4
plants
6
Reactions of the oxidative photosynthetic carbon
(C2) pathway
7
Xylem and phloem transport streams can be sampled
by several methods
8
Xylem and phloem transport streams can be sampled
by several methods
9
Diagram of the apoplast / symplasm concept in its
simplest form
10
Diagram showing patterns of xylem and phloem
transport
11
Important sites of xylem-to-phloem solute
transfer occur at leaf traces and in minor veins
of leaves
12
(A) Electron micrographs of plasmodesmata in
longitudinal and cross-sections, accompanied by
the terminology aoolied to frequently observed
structural features. (B) A model of plasmodesmal
substructure based on observations of
freeze-substituted tobacco leaves
13
Companion cell (CC) and a sieve element (SE) are
connected by a pore-plasmodesma complex
consisting of a pore in the sieve element wall
linked via a central cavity to multiple
plasmodesmata in the companion cell wall (CW)
14
Conceptual models for the cell-to-cell
trafficking of viral RNA(vRNA)
15
V-type H-ATPase
16
Overview of N uptake by a nonnodulated plant
(left), and by a nodulated plant with N-fixing
symbionts (right)
17
(A) Domain structure of nitrate reductase. (B)
Ribbon diagram of nitrate reductase
18
Proposed model for regulation of nitrate
reductase activity by phosphorylation /
dephosphorylation and reversible binding of
14-3-3 protein
19
Overview of sulfur uptake, reduction, and
transport in plants
20
Structures of representatives from the nine types
of plant hormones discussed in this chapter
21
Structure of gibberellic acid, GA3
22
Structures of C20 - GAs and C19 - GAs
23
Structures of some of the GAs that have been
tested in various GA bioassays and that have
yielded data providing key information on the
strict structural requirements of GA receptor
site
24
Effect of GA3 on stem elongation of Progress No.9
dwarf pea seedlings (left) control plants,
(right) plants seven days after treatment with 5
mg of GA3
25
Promotion of leaf sheath elongation of Tanginbozu
dwarf rice three days after treatment with GA3
(left) control (center) 100 pg of GA3 per
seedling (right) 1 ng of GA3 per seedling
26
Terpenoid biosynthesis pathway, showing the
biosynthetic origins of GAs as well as
cytokinins, brassinosteroids, and abscisic acid
27
Metabolism of GA20 leads to formation of
biologically active GAs that are then deactivated
in different species by various routes
28
Structures of ABA enantiomers. (S)- ABA is the
naturally occurring form
29
Precocious germination (vivipary) of immature
seed of ABA-insensitive vp1 mutant of maize
30
ABA-induced stomatal closure
31
Summary of two possible biosynthetic routes to ABA
32
(A) Kinetin is a synthetic cytokinin generated
when DNA is autoclaved. (B) Zeatin was the ferst
endogenous cytokinin isolated from plants. (C) N6
Benzyladenine (BA) is a synthetic compound with
cytokinin activity
33
Arabidopsis callus production is induced by
placing tissue on medium containing auxin (IBA)
and cytokinin
34
Cytokinin oxidases remove the side chains from
cytokinin molecules
35
Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), the auxin most widely
distributed among plants, and related compounds
36
L-Tryptophan-dependent IAA biosynthesis pathways
37
Nondecarboxylative catabolism and conjugation of
IAA in seedlings of Zea mays and Vicia faba
38
Wild-type plant (left) IAA-over-producing plant
expressing Agrobacterium tumefaciens iaaH and
iaaM genes under the control of the CaMV 35s
promoter (right).
39
The triple response to ethylene of six-day-old
etiolated pea seedlings and four-day-old
etiolated mung bean seedlings
40
The methionine cycle and ethylene biosynthesis
41
Effect of antisense ACC-oxidase genes on the
ripening and spoilage of Ailsa Craig tomatoes in
fruits picked three weeks after the onset of
ripening and stored at room temperature for three
weeks