Axial and Equatorial positions are not energetically equivalent - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
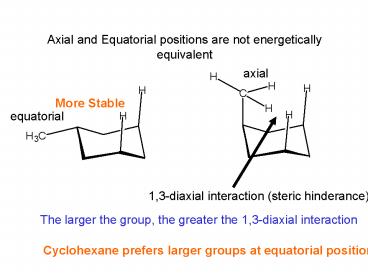
Axial and Equatorial positions are not energetically equivalent
Description:
... interaction (steric hinderance) More ... Cyclohexane prefers larger groups at ... Need to consider cis and trans and equatorial and axial for chair ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:99
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Axial and Equatorial positions are not energetically equivalent
1
Axial and Equatorial positions are not
energetically equivalent
axial
More Stable
equatorial
1,3-diaxial interaction (steric hinderance)
The larger the group, the greater the 1,3-diaxial
interaction
Cyclohexane prefers larger groups at equatorial
positions
2
Conformation Possibilities of 1,3-dimethylcyclohex
ane
Need to consider cis and trans and equatorial and
axial for chair conformation
trans
cis
2 methyls axial
1 methyl axial 1 methyl equatorial
2 methyls equatorial
3
Halogenation of Alkanes a useful method for
making alkanes more reactive
By adding an electronegative atom to the chain,
it creates a reactive site
Depending on X, a variety of products can be
produced
Bromination is the one halogen that adds
selectively, or in other words we know where it
is going to add
4
Selectivity can mean many things with chemical
reactions.One of the most common selectivities
associated with chemical reactions is a
preference, or selectivity, toward carbons with
different number of carbon-carbon bonds
Methyl carbon - bonded to 0 carbon 1(primary)
carbon - bonded to 1 carbon 2(secondary) carbon
- bonded to 2 carbons 3(tertiary) carbon -
bonded to 3 carbons 4(quaternary) carbon -
bonded to 4 carbons
1
1
3
1
4
2
1
1
5
Selective Halogenation via Bromination
Chlorination is not selective,mixtures of
products are obtained
Table 3-6 p. 115
Relative Reactivities Toward Halogenation
Mixture of products
2 favored over 1
3 favored over 1 or 2
6
Energy Changes in Halogenations - Why Bromination
Selective?
chlorination
fluorination
1 route
1 route
2 route
3 route
bromination
Only one with endothermic first step, therefore
reaction can be heated slowly to get better
selectivity
1 route
3 route
7
Bond Dissociation Energies- DH DH
For Bromination
1
2
3
Tertiary radicals are the most stable-lowest
energy
E
Tertiary C-H bond is the weakest of the three.
Therfore, easiest to break, lowest energy change
Time
8
Where do we get our chemicals from?
Some we grow(corn-ethanol) or dig-up(CaCO3) and
use as is. Many come from reactions beginning
with ethanol Most come from petroleum!
Petroleum consists of hydrocarbon (alkanes)
chains ranging from C1 to gtC25
As for chemical reactivity, alkanes are quite
unreactive and unselective in their reactions
9
Controlling the Selectivity of Alkane Reactions
First step is distillation of components of crude
oil
Natural gas, gasoline lower boiling points Diesel
fuel, waxes higher boiling points
Second step is Cracking and Reforming
Zeolites act as catalysts that break down (crack)
large chains and assemble (reform) more useful
products
Cracking - C16 wax or grease cracked to a C8
wax or grease
Reforming
heptane
toluene
10
Zeolite Structure
Combination of aluminum oxide and silicon oxide
The channels provide for the size-selectivity of
cracking and reforming
11
The Ozone Story
These two reactions filter the harmful UV
radiation from reaching the surface of the planet
CFCs - chlorfluorocarbons
CFC-12 (air conditioning)- CCl2F2
The CFC-12 molecule can also cleave in the
presence of light
Note Add 90 to , this will indicate of CHF,
the remainder is Cl, letters represent different
isomers
Ex 12 90 102, 1 carbon, 0 hydrogen, 2
fluorine, and then 2 chlorine
12
Steps in O3 Depletion
O3 O
2O2
Initiation
h?
CCl2F2
CClF2 Cl
Propagation
ClO O2
Cl O3
Cl O2
ClO O
Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic?
13
Energetics of Ozone Depletion
O3 O
2O2
O-O 33 kcal/mol Cl-O 49 kcal/mol OO 119 kcal/mol
Dissociation energies
ClO O2
Cl O3
?H O-O broken - Cl-O made 33 - 49 -17
kcal/mol
Cl O2
ClO O
?H Cl-O broken - OO made 49 - 119 -70
kcal/mol
Total energy change(?H) is summation of ?H of
each step -17 -70 -87 kcal/mol -
Exothermic
Exothermic reactions are generally quite favored!