Reaction Rate Theory - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title:
Reaction Rate Theory
Description:
Similarly can we separate the internal motions of a molecule in ... There may also be steric. hindrance leading to. reduced S. IC. T. IC-17 /26 Lecture-4B 30-0910-2004 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:59
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Reaction Rate Theory
1
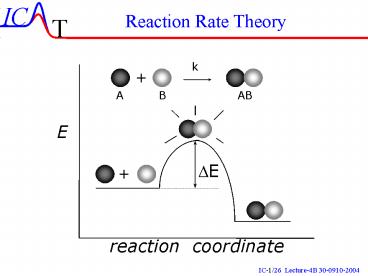
Reaction Rate Theory
2
Partition Functions
Similarly can we separate the internal motions of
a molecule in Part involving vibrations, rotation
and nuclei motion, and electronic motion i.e.
for a mulecule we have
Now we create a system of many molecules N that
are in principle independent and as they are
indistinguishable we get an overall partition
function Q
3
Partition Functions Summary
s
4
Partition Functions
What was the advantage of having the Partition
Function?
5
Surface Collisions
Consider a box with volume V
What are the numbers?
6
Surface Collisions
How many are successful in reacting? Simple
Maxwell-Boltzman distribution
7
Transition State Theory
Consider the following reaction
q
How?
We assume that R and R are in Equilibrium
8
Transition State Theory
By splitting the partition function in the
transition state
9
Transition State Theory
The partition function q can conveniently be
split further
Which basically is the Arrhenius form If q0 q
n 1x1013s-1
Relation to Thermodynamics
10
Transition State Theory
Think of some examples
Temperature dependence of prefactor
11
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
Indirect adsorption of atoms
An atom adsorbs into a 2-dim mobile state, we
have Ng gas atoms, M sites on the surface, and N
atoms in the transition state
12
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
Now what is K ?
13
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
This corresponds to the collision on a surface
since the atoms are still free to move in two
dimensions
14
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
Direct adsorption of atoms
M is total number of sites M is number of free
sites
Why?
15
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
16
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
Notice adsorption always result in loss of entropy
There may also be steric hindrance leading to
reduced S
17
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
What happens in the regime between direct and
indirect adsorption?
The atoms breaks free of the site and start to
diffuse around in
18
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
Indirect adsorption of molecules
Notice that if the precursor is sufficiently
loose S0(T)1.
19
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
Direct adsorption of molecules
20
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
21
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
22
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
23
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
Notice how the Keq is alone determined from
initial and final state partition functions.
24
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
Desorption
25
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
System Prefactor s-1 Ea
kJ/mol CO/Co(0001) 1015
118 CO/Ni(111) 1015
130 CO/Ni(111) 1017
155 CO/Ni(111) 1015
126 CO/Ni(100) 1014
130 CO/Cu(100) 1014
67 CO/Ru (001) 1016
160 CO/Rh(111) 1014 134
How?
26
Transition State Theory on Surfaces
If the details of the transition state can be
determined can the rate over the barrier be
calculated.
- Details of the transition state are difficult to
access - Low concentration
- Short lifetime.
Often determined by First Principle
calculations, but are only accurate to say 0.1
eV or 10 kJ/mol.