Tools to generate data for Bioinformatics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title: Tools to generate data for Bioinformatics
1
Tools to generate data for Bioinformatics
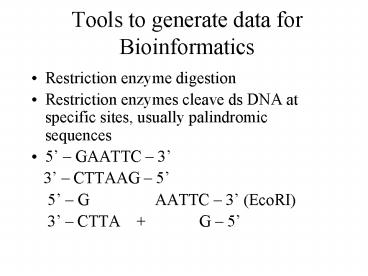
- Restriction enzyme digestion
- Restriction enzymes cleave ds DNA at specific
sites, usually palindromic sequences - 5 GAATTC 3
- 3 CTTAAG 5
- 5 G AATTC 3 (EcoRI)
- 3 CTTA G 5
2
- The EcoRI digestion generated sticky ends
- The sticky ends can be covalently joined back
together using DNA Ligase - Restriction enzymes that do not create sticky
ends can create blunt ends - Example Hind II cleaves
- 5 - G T Py Pu A C 3
- 3 - C A Pu Py T G -5
3
(No Transcript)
4
- Gel electrophoresis uses an agarose gel to
separate DNA or RNA fragments according to size - The DNA or RNA is blotted or transferred to a
nylon membrane - A radiolabeled DNA probe (usually 20 nts) is
allowed to hybridize to DNA or RNA on the nylon
membrane - The nylon membrane is exposed overnight to x-ray
film.
5
(No Transcript)
6
- Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
- Restriction sites occur randomly in genomic with
the probability of P (1/4)n where n number of
nucleotides (usually 6 for restriction enzymes) - So restriction site should occur about every
4,096 nts
7
- Sometimes a mutation occurs which destroys the
restriction site. - This results in a different pattern of DNA
fragments from being generated than expected. - We can use this unexpected pattern of DNA
fragments to identify individuals. - Thus RFLP can be used in forensic analysis
8
MicroArray
- Short pieces of known DNA are arranged on a nylon
membrane as a grid. - mRNA from the target (i.e. tumor cells) is used
as a template to synthesize cDNA - The cDNA is synthesized using the reverse
transcriptase - The cDNA is labeled with flouresecent dyes and
allowed to hybridize to the DNA on the nylon. - The intensity of the resulting signal shows the
relative abundance of the RNA
9
(No Transcript)
10
- DNA fragments can be cloned into vectors (i.e.
plasmids, lamda phage, Cosmids, Yeast Artificial
Chromosomes (YACS) - Genomic libraries can be constructed from the
total genomic DNA inside cells. - Genomic libraries usually use lambda phage,
Cosmids and YACS - cDNA libraries are constructed from cDNA
synthesized from total mRNA templates
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
- Traditional genomic and cDNA libraries allow only
one sequence to be searched at a time. - Hybridization of the probe to the target is only
the first step. The target must be isolated and
sequenced before analysis can begin. - Low abundance targets in library may easily be
missed by the probe.
15
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- Highly sensitive technique for detecting low
abundance DNA fragments - Advantages quick (about 2 hours), inexpensive,
requires little training - Disadvantages only amplifies (copies) DNA
fragments ( whose size less than 1.5 Kb), easily
contaminated with previously PCR amplified DNA
16
PCR steps
- DNA is heated to 92oC to denature the DNA
- DNA is cooled to 54oC to allow the DNA primers to
anneal to the single stranded DNA - Temperature is raised to 72oC to allow Taq
polymerase (DNA polymerase) to synthesize new DNA
strand - Repeat previous steps 30 times
17
(No Transcript)