The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 43
Title:
The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
Description:
Early Events in the Mammalian Cell Cycle. MB. 523. CycD1. Cdk4,6. E2F. CycE. DNA Replication Genes ... Upregulated in senescent cells, which arrest at G1 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:518
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
1
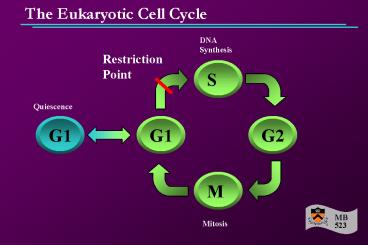
The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
DNA Synthesis
Restriction Point
Quiescence
Mitosis
2
Cyclins, Cdks and the Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
Cdk4,6
Cdk2
Cdk1
Cdk2
Cdk1
3
Early Events in the Mammalian Cell Cycle
SCF
Mitogen
p27
CycD1
Cdk4,6
CycD1
Cdk4,6
Rb
Rb
E2F
E2F
CycE
E2F
Rb
E2F
CycD
DNA Replication Genes
4
Early Events in the Mammalian Cell Cycle
SCF
Mitogen
p27
CycD1
Cdk4,6
CycD1
Cdk4,6
Rb
Rb
E2F
E2F
CycE
E2F
Rb
E2F
CycD
DNA Replication Genes
5
Early Events in the Mammalian Cell Cycle
SCF
Mitogen
p27
CycD1
Cdk4,6
CycD1
Cdk4,6
Rb
Rb
E2F
E2F
CycE
E2F
Rb
E2F
CycD
DNA Replication Genes
6
Early Events in the Mammalian Cell Cycle
SCF
Mitogen
CycD1
Cdk4,6
CycD1
Cdk2
Cdk4,6
Rb
Rb
E2F
E2F
CycE
E2F
Rb
E2F
CycD
DNA Replication Genes
7
Early Events in the Mammalian Cell Cycle
SCF
Mitogen
CycD1
Cdk4,6
CycD1
Cdk2
Cdk4,6
Rb
Rb
E2F
E2F
CycE
E2F
Rb
E2F
CycD
DNA Replication Genes
8
Early Events in the Mammalian Cell Cycle
S-Phase and Beyond
9
E2F Regulation
10
E2F Family Portrait
11
E2F Activated Genes
- Cyclin E
- Cyclin A
- p107 (Rb-like)
- Cdc2
- ORC1
- Cdc6
- TS (thymidine synthase)
- TK (thymidylate kinase)
- DNA Pol a
Cell Cycle Regulation
DNA Synthesis
12
E2F Associated Genes by ChIP
E2F
4
1
4
1
4
1
4
1
Cell Cycle
Mitosis
DNA Repair
Miscellaneous
DNA Replication
Miscellaneous
Chromatin
Checkpoint
13
Redundancy of E2F Family
E2F1, 2, 3 function as activators while E2F4, 5
function as repressors
14
Redundancy of E2F Family
E2F1-/-, E2F2-/-, lox-E2F3-lox/lox-E2F3-lox
retroviral cre
15
Redundancy of E2F Family
E2F1-/-, E2F2-/-, lox-E2F3-lox/lox-E2F3-lox
E2F1/, E2F2/, E2F3/
-cre
cre
Loss of E2F activity causes arrest throughout the
cell cycle.
16
Redundancy of E2F Family
E2F1-/-, E2F2-/-, lox-E2F3-lox/lox-E2F3-lox
E2F1/, E2F2/, E2F3/
-cre
cre
Loss of E2F activity causes arrest throughout the
cell cycle.
17
KIPs and CIPs and the Cell Cycle
- Inhibits all CDK/Cyclin pairs
- p21CIP1 Induced by p53 in response to DNA damage
- Induction causes arrest at any stage of the cell
cycle - p27KIP1 Required for growth regulation
- p27-/- mouse multiorgan hyperplasia
increased body size no tumors - p57KIP2 Involved in growth regulation
- p57-/- mouse neonatal lethal
developmental defect no tumors
18
The INK4 Family
- Inhibit CDK4/CDK6 Activity Only
- Four Members - Different expression patterns
- p16INK4a - increased in senescence oncogenic
stimuli - p15INK4b - induced by TGFb
- p18INK4c - cell cycle regulated (high in S)
- p19INK4d - cell cycle regulated (high in S)
- Only p16INK4a found mutated in tumors
19
The INK4/CyclinD/CDK4/Rb Pathway
p16INK4a
D1
CDK4/D1
Rb
Rb-P
G1
M
S
20
The INK4/CyclinD/CDK4/Rb Pathway
Primary Regulatory Circuit for Traversing the G1
Restriction Point
- Rb-/- cells do not require Cyclin D for
proliferation - Overexpression of p16INK4a does not inhibit
proliferation of Rb-/- cells - Tumors with mutations in one pathway component
do not acquire mutations in either of the other
components
21
Cyclin D1 and Cancer
- B cell lymphomas - Ig heavy chain enhancer
translocated to intact D1 locus - Amplification of 11q13 (D1 locus)
- squamous cell carcinomas of head and neck (43)
- esophageal carcinomas (34)
- bladder cancer (15)
- primary breast carcinomas (13)
- small cell lung carcinomas (10)
- hepatocellular carcinomas (10)
- Overexpression of D1 in mouse mammary epithelial
cells ductal hyperproliferation and tumors
22
INK4a and Cancer
- Inactivated in most tumor types (25-70)
- 98 of pancreatic carcinomas have inactivated
p16 - Inactivation occurs by homozygous deletion
deletion of one allele and mutational
inactivation of the other or by deletion of one
allele and methylation-associated silencing of
the other - Inactivated in most (gt75) cell lines
- INK4a-/- mouse high incidence of
spontaneous and carcinogen induced tumors
cooperates with Ras to induce melanomas
23
Redundancy of Rb Family in p16 Inhibition
Inhibition of growth by p16INK4a requires both Rb
and p107 or p130
Rb-P
E2F-1
E2F-2
Rb
Cdk4,6
S
E2F-3
p16
ClnD
p107, p130
E2F-4
E2F-5
p107-P, p130-P
24
Activation of p16INK4a
- Cellular senescense
- Upregulated in senescent cells, which arrest at
G1 - p16 upregulated in SV40 transformants at time of
senescence, even though senescence doesnt occur - Loss of INK4a facilitates immortalization of
many cell types - Ras oncogene activation
- Premature senescence induced by Ras
transformation of primary fibroblast - Requires p53 and INK4a
25
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
Transcript a
p16INK4a
1b
1a
2
3
Transcript b
p19ARF
26
p19ARF Blocks MDM2 Inhibition of p53
- p19ARF G1 Arrest Requires p53
- p19ARF RasMyc or E1aRas
Transformation Requires p53 - p19ARF MDM2 Transformation Requires p53
- p19ARF binds to Mdm2 in vivo and sequesters it
in the nucleolus - p19ARF during growth in culture and ARF-/-
MEF cells do not undergo senescence in culture
27
MDM2 Inhibition of p53
p53
- Repression of Transcriptional Activation
p21, etc.
28
MDM2 Inhibition of p53
p53
- Repression of Transcriptional Activation
p21, etc.
- Ubiquitin Ligase Activity
p53
29
ARF Localizes to the Nucleolus
30
ARF Relocalized HDM2 to the Nucleolus
31
ARF Stabilizes p53 From Mdm2-Induced Turnover
Arf prevents Mdm2-induced export of p53 from the
nucleus and subsequent degradation in the
cytoplasm
p53 can be stabilized either by posttranslational
modification or by Arf sequestration of Mdm2
32
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
1b
1a
2
3
Transcript b
Transcript a
p19ARF
p16INK4a
MDM2
p53
pRb
CDK4/6
E2F
p21CIP1
33
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
1b
1a
2
3
Transcript b
Transcript a
p19ARF
p16INK4a
Which Product is the Tumor Suppressor?
The vast majority of INK4a mutations in human and
mouse tumors are Exon 2 deletions, which affect
both p19ARF and p16INK4a.
34
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
Mutations of INK4a/ARF Exon 2 found in human
tumors
Frameshift
INK4/ARF-
INK4-/ARF-
35
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
1b
1a
2
3
Transcript b
Transcript a
p19ARF
p16INK4a
Which Product is the Tumor Suppressor?
- Em-myc induced lymphomagenesis is accelerated
equally in ARF/- and INK4a/ARF/- mice. - Em-myc, ARF-/- mice die of lymphomas within
several weeks of birth
36
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
Loss of p19ARF but not p16Ink4a blocks senescence
of MEFs
37
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
Loss of p16Ink4a alone does not ablate
senescence, increase Ras-induced foci formation
or alter the growth rate of MEFs, but
Em-Myc Induced cancer
Spontaneous cancer
p16Ink4a nonsense mutation at position 101,
silent in p19ARF
38
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
Also
Spontaneous tumors
DMBA-Induced tumors
p16Ink4a-/- Exon 1a deletion
39
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
p16Ink4a Contributes to Chemotherapy Response by
Promoting Drug Induced Senescense
Em-myc induced lymphomas treated with
cyclophosphamine
40
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
p16Ink4a Contributes to Chemotherapy Response by
Promoting Drug Induced Senescense
ARF
control
Ink4a/ARF
bcl2
p53null
bcl2 p53null
bcl2 Ink4a/ARF
bcl2 ARF
Em-myc induced lymphomas treated with
cyclophosphamine
41
INK4a - One Gene, Two Products
p16Ink4a Contributes to Chemotherapy Response by
Promoting Drug Induced Senescense
42
Loss of p18 in Mouse Causes Organomegaly
43
Cooperativity of p18INK4c and p27Kip1
Loss of p18 or p27 leads to intermediate lobe
pituitary hyperplasia and adenomas, while loss of
both yields early onset pituitary tumors