Chapter 13 Review Electrons in Atoms
1 / 14
Title:
Chapter 13 Review Electrons in Atoms
Description:
photons. Chapter 13 Review. Bohr's contribution to the development of ... What is the energy of a photon whose frequency is 5.2 x 1015 s-1? ( 4.8 x 1014 s-1 ) ... –
Number of Views:140
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 13 Review Electrons in Atoms
1
(No Transcript)
2
Chapter 13 Review -Electrons in Atoms
Bohrs planetary model
- Charles Page High School
- Dr. Stephen L. Cotton
3
Chapter 13 Review - definitions
- Aufbau principle
- quantum
- photoelectric effect
- atomic orbitals
- Pauli exclusion principle
4
Chapter 13 Review - definitions
- Energy level
- Hunds rule
- electron configurations
- quantum mechanical model
- photons
5
Chapter 13 Review
- Bohrs contribution to the development of atomic
structure was - What is the total number of orbitals in the third
principal energy level?
(proposed that electrons travel in circular
orbits around the nucleus.)
( 9 )
6
Chapter 13 Review
- What is the maximum number of electrons allowed
in the third energy level - What is the maximum number of electrons that can
occupy one orbital? - What is the electron configuration for fluorine?
( 18 )
( 2 )
( 1s22s22p5 )
7
Chapter 13 Review
- The first 3 electrons that enter into p orbitals
must have - The atom whose electron configuration is
1s22s22p63s23p1 is - The configuration for the outermost energy level
in Ca is
( parallel spins )
( Aluminum )
( 4s2 )
8
Chapter 13 Review
- The element having the same s and p
configurations for principal energy level 3 as
the element F has for its principal energy level
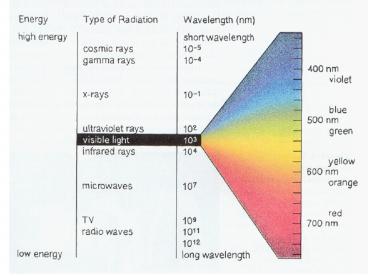
2 is - The frequency and wavelength of all waves are
( Chlorine )
( inversely related )
9
Chapter 13 Review
- The SI unit of cycles per second is called a
- Which have the same outer energy level
configurations a) Li, Be, N, Ne or b) N, P, As,
Bi? - The wavelength of light with a frequency of 2.50
x 1013 s-1 is
( hertz )
( b )
( 1.20 x 10-5 m )
10
Chapter 13 Review
- Once the electron in a hydrogen atom absorbs a
quantum of energy, it - Write the electron configuration for
- Mg
- P
- Br
( is now in its excited state )
( 1s22s22p63s2 )
( 1s22s22p63s23p3 )
( 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p5 )
11
Chapter 13 Review
- Identify the following elements
- 1s22s22p63s23p4
- a full second energy level
- the first d electron
- 7 e-1 in 4th energy level
- only 2 e-1 in 5th energy level
- 3 unpaired e-1 in 3rd level
( sulfur )
( neon )
( scandium )
( bromine )
( Sr )
( P )
12
Chapter 13 Review
- What is the frequency of radiation whose
wavelength is 6.25 x 10- 5 cm? - What is the energy of a photon whose frequency is
5.2 x 1015 s-1?
( 4.8 x 1014 s-1 )
(3.45 x 10-18 J )
13
Chapter 13 Review
- Distinguish between the Bohr model and the
quantum mechanical model, in terms of positions
of the electrons.
( According to the Bohr model, electrons travel
around the nucleus along fixed paths, much as the
planets orbit the sun. The quantum mechanical
model explains the positions of electrons in
terms of probability clouds, within which the
electrons are most likely to be found. )
14
Chapter 13 Review - additional definitions
- Heisenberg uncertainty principle
- wavelength
- ground state
- amplitude
- de Broglies equation
- frequency