Physical Performance Scores - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Physical Performance Scores
Description:
The high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism in ... We hypothesized that vitamin D supplementation to increase 25-OHD levels to ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:103
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Physical Performance Scores
1
Grip Strength Is Improved by Vitamin D
Supplementation in African American Women Melissa
Li-Ng, M.D.,1,3 John F. Aloia, M.D.2 and Jason A.
Wexler, M.D.1,3 1Division of Endocrinology,
Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington,
DC 2Winthrop-University Hospital, Mineola, NY
3Division of Endocrinology, Washington Hospital
Center
Physical Performance Scores
- The Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) was
administered to assess strength, endurance and
balance. Subjects were asked to perform a balance
assessment, a timed 4-meter walk, and a
chair-rise test. The higher the SPPB score, the
better the physical performance. The maximum
SPPB score is 12. - A dosing algorithm developed from a prior study
determined the dose of vitamin D3 based on the
baseline serum 25-OHD level. If the subjects
25-OHD level was mcg of vitamin D3 per day. If her 25-OHD level
was between 45 and 75 nmol/L, she received 70
mcg/day. If her 25-OHD level was 75 nmol/L, she
did not receive any vitamin D supplementation.
- BACKGROUND
- Muscle weakness is a prominent feature of the
clinical syndrome of vitamin D deficiency. - Randomized clinical trials have shown improved
muscle strength and reduced risk of falling in
elderly women supplemented with vitamin D and
calcium. - Lower 25-hydroxyvitamin (25-OHD) concentration
and a higher parathyroid hormone (PTH)
concentration are associated with loss of grip
strength and muscle mass. - The high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and
secondary hyperparathyroidism in African
Americans could influence the loss of muscle mass
and strength with aging in this population. - Older African Americans have not been studied in
vitamin D intervention trials. - HYPOTHESIS
- We hypothesized that vitamin D supplementation to
increase 25-OHD levels to optimal levels 75
nmol/L will result in improvement in strength and
physical performance in older African American
women. - AIMS
- The primary aim of this study was to answer the
following question Does vitamin D
supplementation influence physical performance in
African American women? - METHODS
- A cohort of African American postmenopausal women
that participated in a previous study on vitamin
D and bone density were invited to participate.
African American ancestry was assessed by
self-declaration. - Participants had a baseline history and physical
and 3 follow-up visits at 1 week, 2 months, and 4
months. - Grip strength was measured using a handgrip
dynamometer. Isometric grasp was measured in the
dominant hand. The mean of three measurements was
recorded.
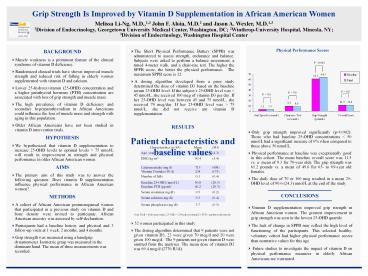
P
P NS
P NS
P NS
RESULTS Patient characteristics and baseline
values
- Only grip strength improved significantly
(pconcentrations increase of 6 when compared to those above 50
nmol/L. - Physical performance at baseline was
exceptionally good in this cohort. The mean
baseline overall score was 11.5 vs. a mean of
9.3 for 70-year olds. The grip strength was 61.2
pounds vs. a mean of 49.6 for 65- to 69-year old
females. - The daily dose of 70 or 100 mcg resulted in a
mean 25-OHD level of 90.6 (24.3) nmol/L at the
end of the study.
Note BMI body mass index 25-OHD
25-hydroxyvitamin D PTH parathyroid hormone
- 52 women participated in this study.
- The dosing algorithm determined that 9 patients
were not given vitamin D3, 23 were given 70 mcg/d
and 20 were given 100 mcg/d. The 9 patients not
given vitamin D were omitted from the analyses.
The mean dose of vitamin D3 was 69.4 mcg/d (2776
IU/d).