Kinetics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title:
Kinetics
Description:
Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm: KA pA. 1 KA pA. IC-14 /38 Lecture-3 16-09-2004. Adsorption ... Langmuir Isotherm. 1927. Kinetics of Catalytic Reactions. Cyril ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:919
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Kinetics
1
Kinetics
2
What is Kinetics ?
- Analysis of reaction mechanisms on the molecular
scale - Derivation of rate expressions
- Design and analysis of experiments to test rate
equations and derive kinetic parameters - Theoretical prediction of rate constants
- How can we improve it?
3
Basic surface interactions
- Reactions take place on the metal surface
4
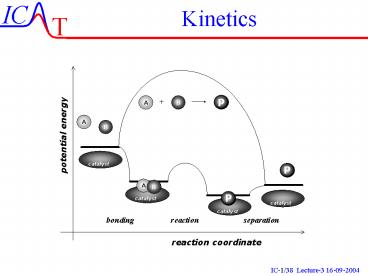
Reaction Scheme
- Reaction
O2
CO
CO2
catalyst
Adsorption
Desorption
Reaction
Energy
adsorption
reaction
desorption
reaction coordinate
5
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Adsorption
Reaction
Desorption
6
The Mean-FieldApproximation
Ntotal number of sites NANumber of sites
occuppied by A NBNumber of sites occuppied by
B NNumber of free sites
?ANA/N ?BNB/N ?(N-NA-NB)/N
7
Monte Carlo Simulations
- r ltlt N k ?A?B
8
Experimental Evidence by STM
a
b
8x8 nm
9
The Heat of Adsorption is Always
- Negative !!!!
Negative !!!!
10
Reaction Scheme
- Reaction
O2
CO
CO2
catalyst
Adsorption
Desorption
Reaction
Energy
adsorption
reaction
desorption
reaction coordinate
11
Adsorption
- Associative Adsorption CO, N2, Ar, He, etc
At equilibrium
12
Langmuir Isotherm
13
Irving Langmuir(1881 - 1957)
- worked at General Electrics
- oxygen adsorption on tungsten
- filaments of light bulbs
- 1932 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
- Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm
KA pA
?A
1 KA pA
14
Adsorption
- Dissociative Adsorption N2, O2, CO, H2 etc.
For equilibrium 0
15
Adsorption
- Competitive Adsorption
16
The Fuel Cell
17
CO severely reduces efficiency
18
Langmuir - Hinshelwood Kinetics
Cyril Norman Hinshelwood 1897 - 1967 Nobel Prize
1956
19
Eley - Rideal Mechanism
direct reaction between gas phase and adsorbed
species
Unlikely !!
20
The Langmuir-Hinselwood (LH) mechanism
Net reaction over catalyst
Elementary steps
21
The Complete Solution
22
The Steady State Approximation
Interesting solution for many processes, but we
lose time dependence
Last eq. not independent, i.e. n-1 eq. for n
elementary steps
23
The Quasi-equilibrium Approximation
Assumes one step is rate limiting while the rest
are in Quasi-equilibrium
RLS
24
The Quasi-equilibrium Approximation
Notice only valid when step 3 is rate limiting!
25
Steps with Similar Rates
Assume step 1 and 3 are slow i.e. rate limiting
steps (rls)
while step 2 and 4 are in quasi-equilibrium
Resulting in a reduced problem as comparred to
the complete solution
26
Simplifications to the Quasi-equilibrium
Approximation Irreversible steps
How does this approximation describe the approach
towards equilibrium?
27
Simplifications to the Quasi-equilibrium
Approximation The MARI Approximation
The Most Abundent Reaction Intermediate
approximation (MARI)
Assume for example that specie A bonds much
stronger than B and AB- A will then become MARI
What are examples of MARI??
28
Simplifications to the Quasi-equilibrium
Approximation Nearly empty Surface
Typical for high temperatures
In that case is it simple to find the maximum of
the rate as a function of gas-composition
29
Reaction order
What is the reaction order nAB?
30
Apparent activation energy as function of
molefraction
31
Apparent activation energy as function of
molefraction
Asumptions
p are assumed independent of T, i.e. we keep the
pressure fixed.
Notice that n3 and DSx both depends on T, but in
a more weak manner than exponential. It can give
problems in an Arrhenius plot.
32
Coverage and reaction order and apparent
activation energy as function of molefraction
Notice nA, nB, and Eapp varies with pressure for
fixed temperature
33
CO Oxidation Reaction Scheme
The overall reaction is
The elementary step on a surface are
34
CO Oxidation the mechanics
For the 3 elementary steps in Quasi equilibrium
we easily obtain the langmuir equation for
adsorption and desorption
35
CO Oxidation- the rate
The rate limiting step
From equilibrium we have
36
CO Oxidation- Temperature limits
The CO2 interacts so weakly that step 4 can be
considered irreversible
Low Temperature limit CO will become MARI
Find reaction orders in this limit.
nO20.5, nCO-1
37
CO Oxidation- Temperature limits
The CO2 interacts so weakly that step 4 can be
considered irreversible
High Temperature limit Very low concentration of
surface species
Find reaction orders in this limit.
nO20.5, nCO1
38
CO Oxidation-Results