Problem Description
1 / 1
Title: Problem Description
1
Building a Prototype Gantry-Tau Parallel Robot
Matthew Murray Supervisor Dr. Geir Hovland
Problem Description Current manufacturing methods
are largely dominated by the use of serial
kinematic machines such as Computer Numerical
Controlled (CNC) Milling Machines. The
manufacturing industry is in need of new machines
to provide greater accuracy and much larger
workspaces than is currently available. The aim
of this thesis is to design a new Parallel
Kinematic Machine (PKM) that can provide fast,
accurate tool point positioning over a 1m cubic
workspace. Solution To meet this demand in the
manufacturing sector Matthew Murray and Matthew
St. Clair have chosen to Build a Prototype
Gantry-Tau PKM under the guidance of Dr. Geir
Hovland. This is the first prototype of a
Gantry-Tau structure ever to be built. A PKM is
a structure that is kinematically parallel, in
that all the joints are connected directly to the
tool point. The parallel configuration reduces
the driven mass of the system as all motors and
linear drives are fixed to the supporting frame.
As a result only the joints and platform undergo
movement during operations.
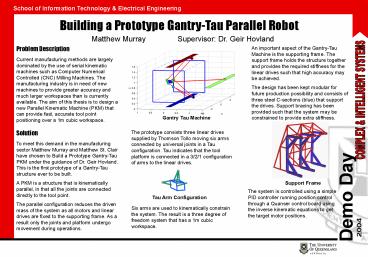
An important aspect of the Gantry-Tau Machine is
the supporting frame. The support frame holds the
structure together and provides the required
stiffness for the linear drives such that high
accuracy may be achieved. The design has been
kept modular for future production possibility
and consists of three steel C-sections (blue)
that support the drives. Support bracing has been
provided such that the system may be constrained
to provide extra stiffness.
Gantry Tau Machine
The prototype consists three linear drives
supplied by Thomson Tollo moving six arms
connected by universal joints in a Tau
configuration. Tau indicates that the tool
platform is connected in a 3/2/1 configuration of
arms to the linear drives. Six arms are used
to kinematically constrain the system. The result
is a three degree of freedom system that has a 1m
cubic workspace.
Support Frame
The system is controlled using a simple PID
controller running position control through a
Quanser control board using the inverse kinematic
equations to get the target motor positions.
Tau Arm Configuration